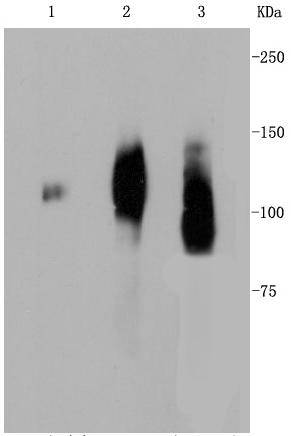
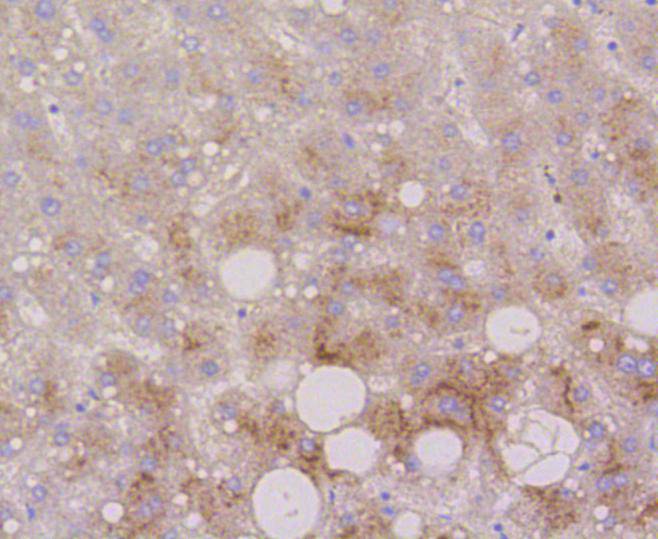
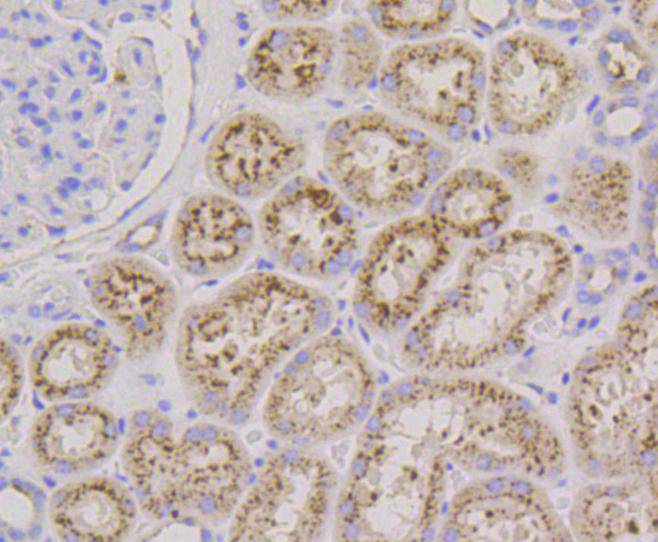
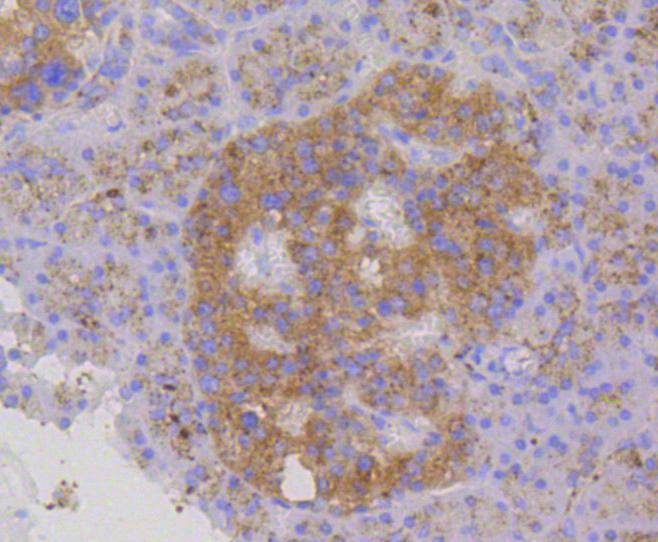
Lysosome-associated membrane proteins (LAMP) are glycosylated type I membrane proteins that play a role in the biogenesis of the pigment melanin. LAMP-1 (also designated CD107A) and LAMP-2 (also designated CD107B) are involved in a variety of functions, including cellular adhesion, and are thought to participate in the process of tumor invasion and metastasis. Newly synthesized LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 proteins are sorted at the trans Golgi network and are transported intracellularly via a pathway that is distinct from the clathrin-coated vesicles used for the mannose-6 phosphate receptor. LAMP-1 is expressed on the surface of thrombin-activated but not resting platelets, and it is thought to be involved in the adhesive, prothrombic properties of these cells. Both LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 are involved in maintaining lysosome acidity and protecting the lysosomal membranes from autodigestion, and their expression is increased in patients with lysosomal storage disorders.