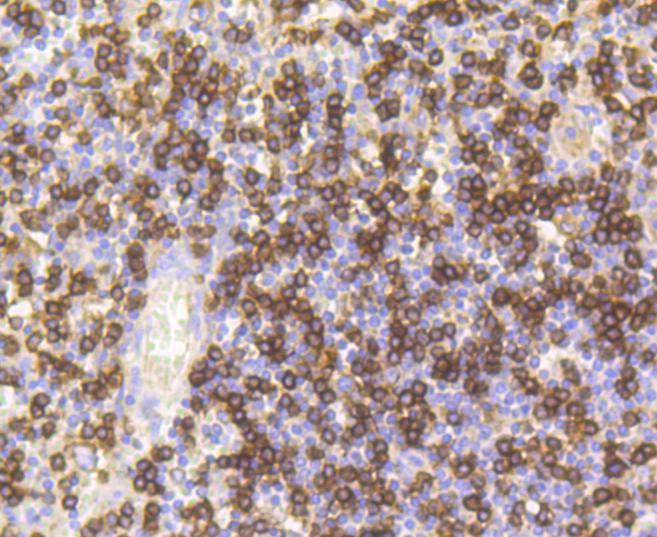
The T cell receptor (TCR) is a heterodimer composed of either α and β or γ and δ chains. CD3 chains and the CD4 or CD8 (CD8-α and CD8-β) co-receptors are also required for efficient signal transduction through the TCR. The TCR is expressed on T helper and T cytotoxic cells that can be distinguished by their expression of CD4 and CD8 proteins; T helper cells express CD4 proteins and T cytotoxic cells display CD8 proteins. CD8s are cell surface glycoproteins that exist as two chain complex (αα or αβ) receptors that bind class I MHC molecules presented by the antigen-presenting cell (APC). A primary function of CD8 proteins is to facilitate antigen recognition by the TCR and to strengthen the avidity of the TCR-antigen interactions. An additional role for CD8-expressing T cells may be to maintain low levels of HIV expression.