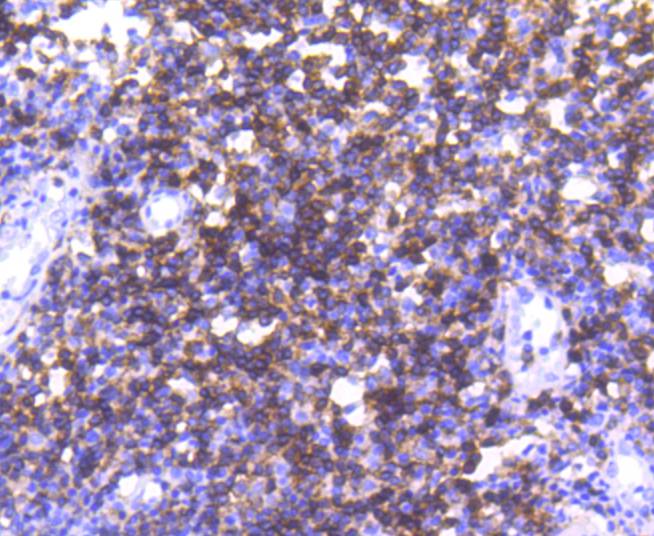
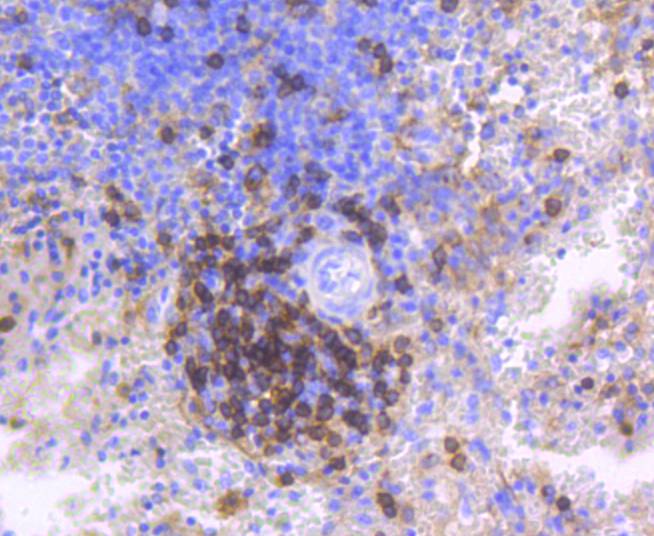
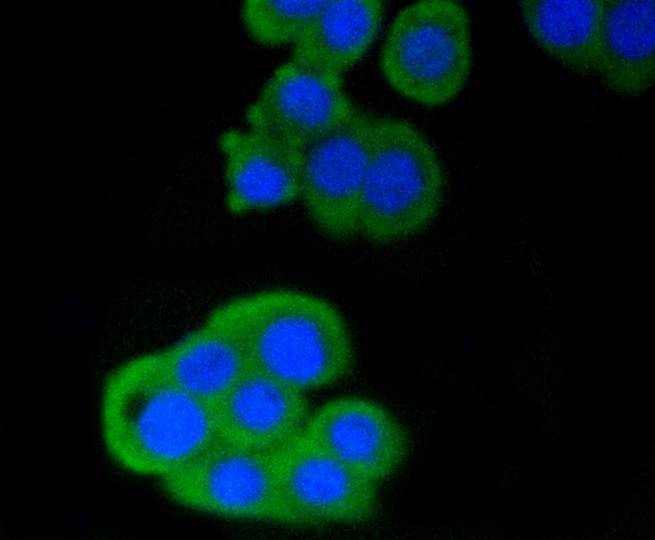
The T cell receptor (TCR) is a heterodimer composed of either α and β or γ and δ chains. CD3 chains and the CD4 or CD8 co-receptors are also required for efficient signal transduction through the TCR. The TCR is expressed on T helper and T cytotoxic cells that can be distinguished by their expression of CD4 and CD8; T helper cells express CD4 proteins and T cytotoxic cells display CD8. CD4 is also expressed on cortical cells, mature medullary thymocytes, microglial cells and dendritic cells. CD4 (also designated T4 and Leu 3), is a membrane glycoprotein that contains four extracellular immunoglobin-like domains. The TCR in association with CD4 can bind class II MHC molecules presented by the antigen-presenting cells. The CD4 protein functions by increasing the avidity of the interaction between the TCR and an antigen-class II MHC complex. An additional role of CD4 is to function as a receptor for HIV.