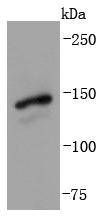
Zinc-finger proteins contain DNA-binding domains and have a wide variety of functions, most of which encompass some form of transcriptional activation or repression. The majority of zinc-finger proteins contain a Krppel-type DNA binding domain and a KRAB domain, which is thought to interact with KAP1, thereby recruiting histone modifying proteins. GLI-1 (GLI family zinc finger 1), also known as Glioma-associated oncogene or oncogene GLI, is a 1,106 amino acid protein that localizes to both the cytoplasm and nucleus, and belongs to the GLI C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family. GLI-1 acts as a transcriptional activator and is thought to play a role in craniofacial development. GLI-1 exists as two alternatively spliced isoforms and is encoded by a gene that maps to human chromosome 12q13.3.