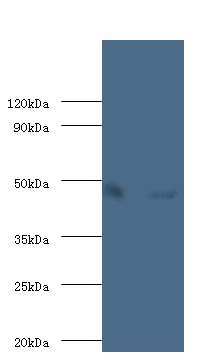
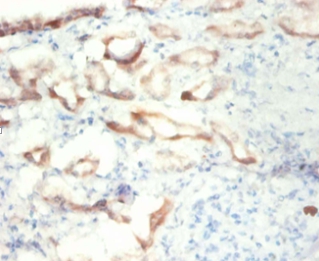
ENO1 encodes one of three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals; it encodes alpha-enolase, a homodimeric soluble enzyme, and also encodes a shorter monomeric structural lens protein, tau-crystallin. The two proteins are made from the same message. The full length protein, the isoenzyme, is found in the cytoplasm. The shorter protein is produced from an alternative translation start, is localized to the nucleus, and has been found to bind to an element in the c-myc promoter. A pseudogene has been identified that is located on the other arm of the same chromosome.
[1] "Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for human alpha enolase."Giallongo A., Feo S., Moore R., Croce C.M., Showe L.C.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83:6741-6745(1986) [2] "Structure of the human gene for alpha-enolase."Gial