Location:
Home
>
Phospho Antibodies > NFκB-p100(Phospho-Ser870) Antibody
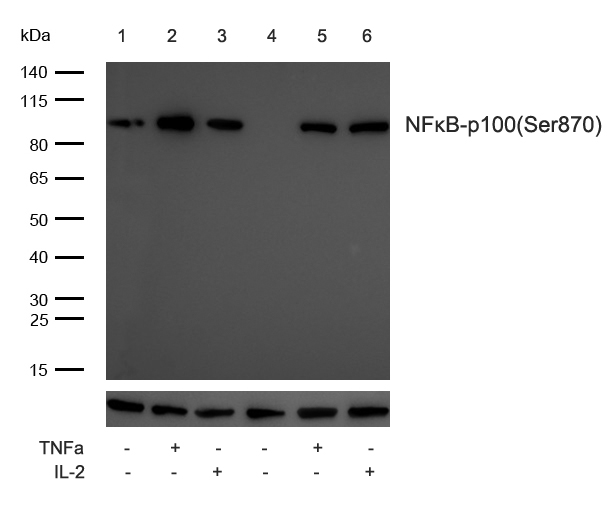
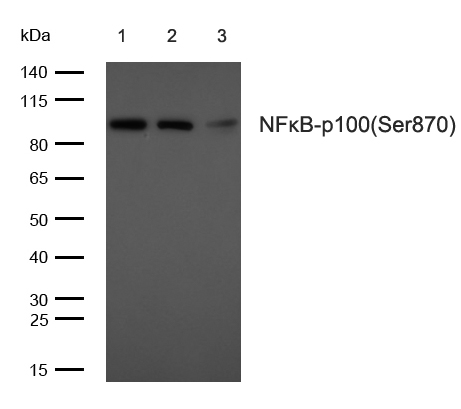
NFκB-p100(Phospho-Ser870) Antibody#11016
NOTE
Application
- WBWestern Blotting
- IHCImmunohistochemistry
- IFImmunofluorescence
- ICCImmunocytochemistry
- FCFlow Cytometry
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- EELISA
- DBDot Blotting
- ChIPChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- GICAGold Immunochromatography Assay
- NCNegative Control
Species Reactivity
- HuHuman
- MsMouse
- RtRat
- DmDrosophila melanogaster
- CCaenorhabditis elegans
- MkMonkey
- RbRabbit
- BBovine
- DDog
- PPig
- HmHamster
- ChHmChinese Hamster
- ChkChicken
- ShpSheep





 Yes
Yes



