Product Detail
Product NameEGFR(Phospho-S695) Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SN07-36
Host SpeciesRabbit
ClonalityMonoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF
Species ReactivityHu
Immunogen DescSynthetic phospho-peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser695 of human EGFR.
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesAvian erythroblastic leukemia viral (v erb b) oncogene homolog antibody
Cell growth inhibiting protein 40 antibody
Cell proliferation inducing protein 61 antibody
EGF R antibody
EGFR antibody
EGFR_HUMAN antibody
Epidermal growth factor receptor (avian erythroblastic leukemia viral (v erb b) oncogene homolog) antibody
Epidermal growth factor receptor (erythroblastic leukemia viral (v erb b) oncogene homolog avian) antibody
Epidermal growth factor receptor antibody
erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 1 antibody
ERBB antibody
ERBB1 antibody
Errp antibody
HER1 antibody
mENA antibody
NISBD2 antibody
Oncogen ERBB antibody
PIG61 antibody
Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1 antibody
Receptor tyrosine protein kinase ErbB 1 antibody
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase ErbB-1 antibody
SA7 antibody
Species antigen 7 antibody
Urogastrone antibody
v-erb-b Avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogen homolog antibody
wa2 antibody
Wa5 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P00533
Uniprot
P00533
Gene ID
1956;
Calculated MW134 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000
ICC: 1:100-1:500
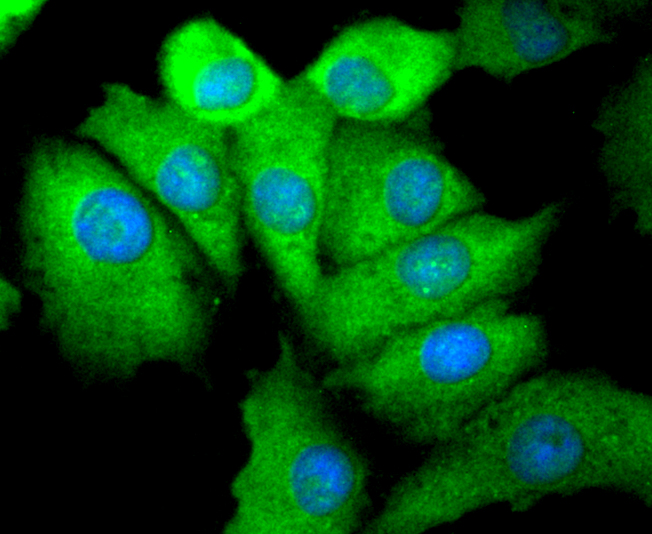
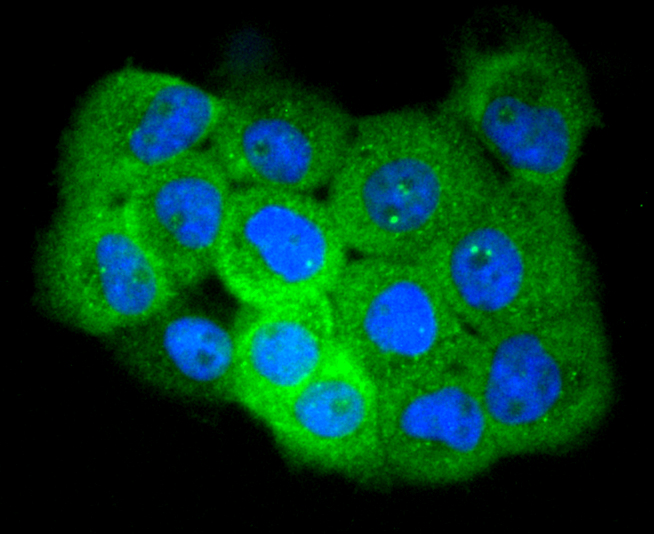
ICC staining Phospho-EGFR(S695) in A549 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
ICC staining Phospho-EGFR(S695) in HUVEC cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
ICC staining Phospho-EGFR(S695) in A431 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
The EGF receptor family comprises several related receptor tyrosine kinases that are frequently overexpressed in a variety of carcinomas. Members of this receptor family include EGFR (HER1), Neu (ErbB-2, HER2), ErbB-3 (HER3) and ErbB-4 (HER4), which form either homodimers or heterodimers upon ligand binding. Exons in the EGFR gene product are frequently either deleted or duplicated to produce deletion mutants (DM) or tandem duplication mutants (TDM), respectively, which are detected at various molecular weights. EGFR binds several ligands, including epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor α (TGFα), Amphiregulin and heparin binding-EGF (HB-EGF). Ligand binding promotes the internalization of EGFR via Clathrin-coated pits and its subsequent degradation in response to its intrinsic tyrosine kinase. EGFR is involved in organ morphogenesis and maintenance and repair of tissues, but upregulation of EGFR is associated with tumor progression. The oncogenic effects of EGFR include initiation of DNA synthesis, enhanced cell growth, invasion and metastasis. Abrogation of EGFR results in cell cycle arrest, apoptosis or dedifferentiation of cancer cells, suggesting that EGFR may be an effective therapeutic target.
If you have published an article using product 13398, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes



