Product Detail
Product NameCD14 Monoclonal Antibody
Host SpeciesMouse
ClonalityMonoclonal
Purificationprotein G purifed
ApplicationsIHC
Species ReactivityHu
Specificityspecific for Recombinant CD14 Protein denatured and native forms
Immunogen Typeprotein
Immunogen DescRecombinant CD14 Protein
Target NameCD14
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesCD14, CD14 molecule
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#: P08571
Uniprot
P08571
Gene ID
929;
Concentration1.0mg/mL
FormulationPreservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
Immunohistochemistry: 1:20 - 1:200
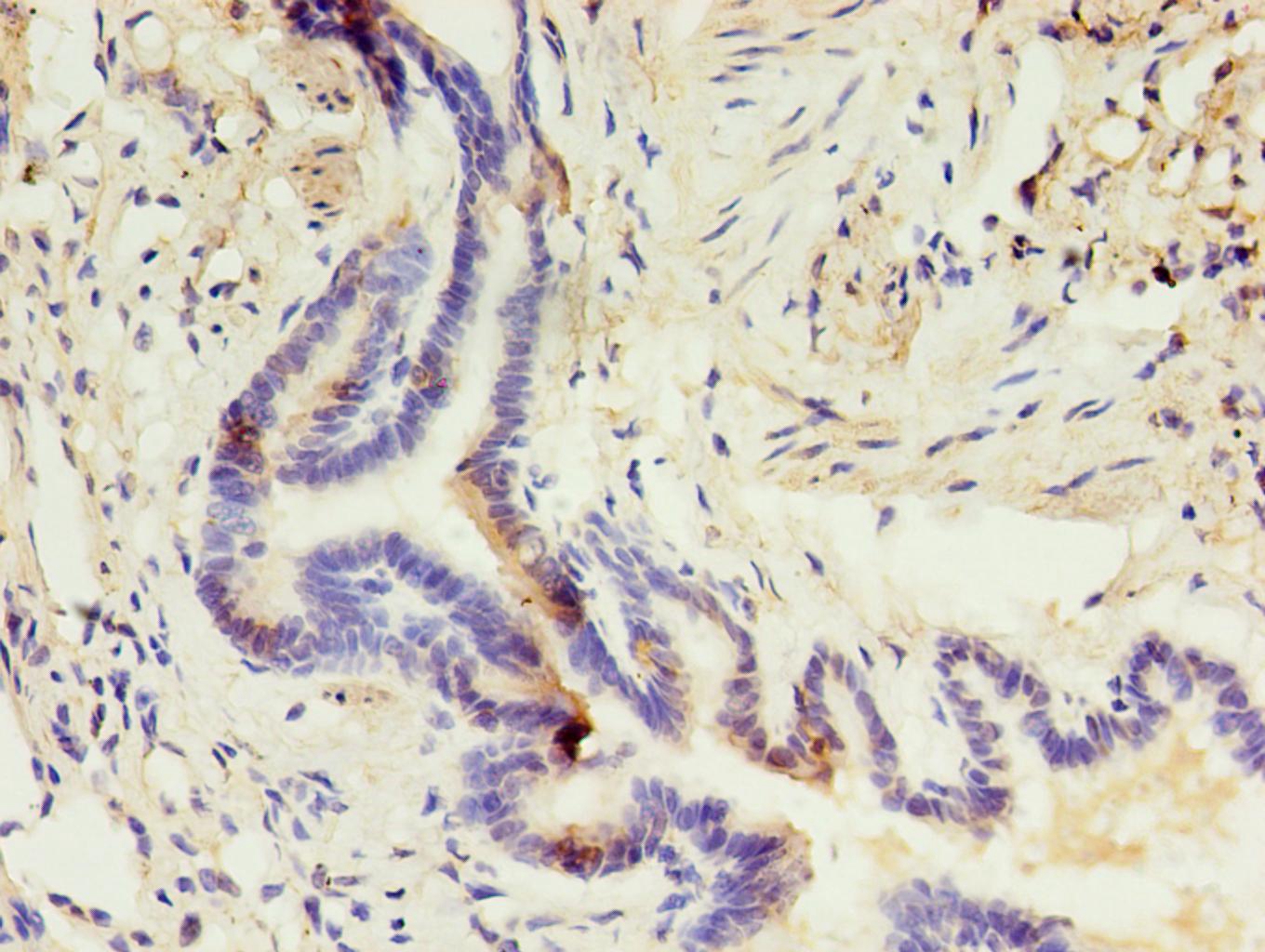
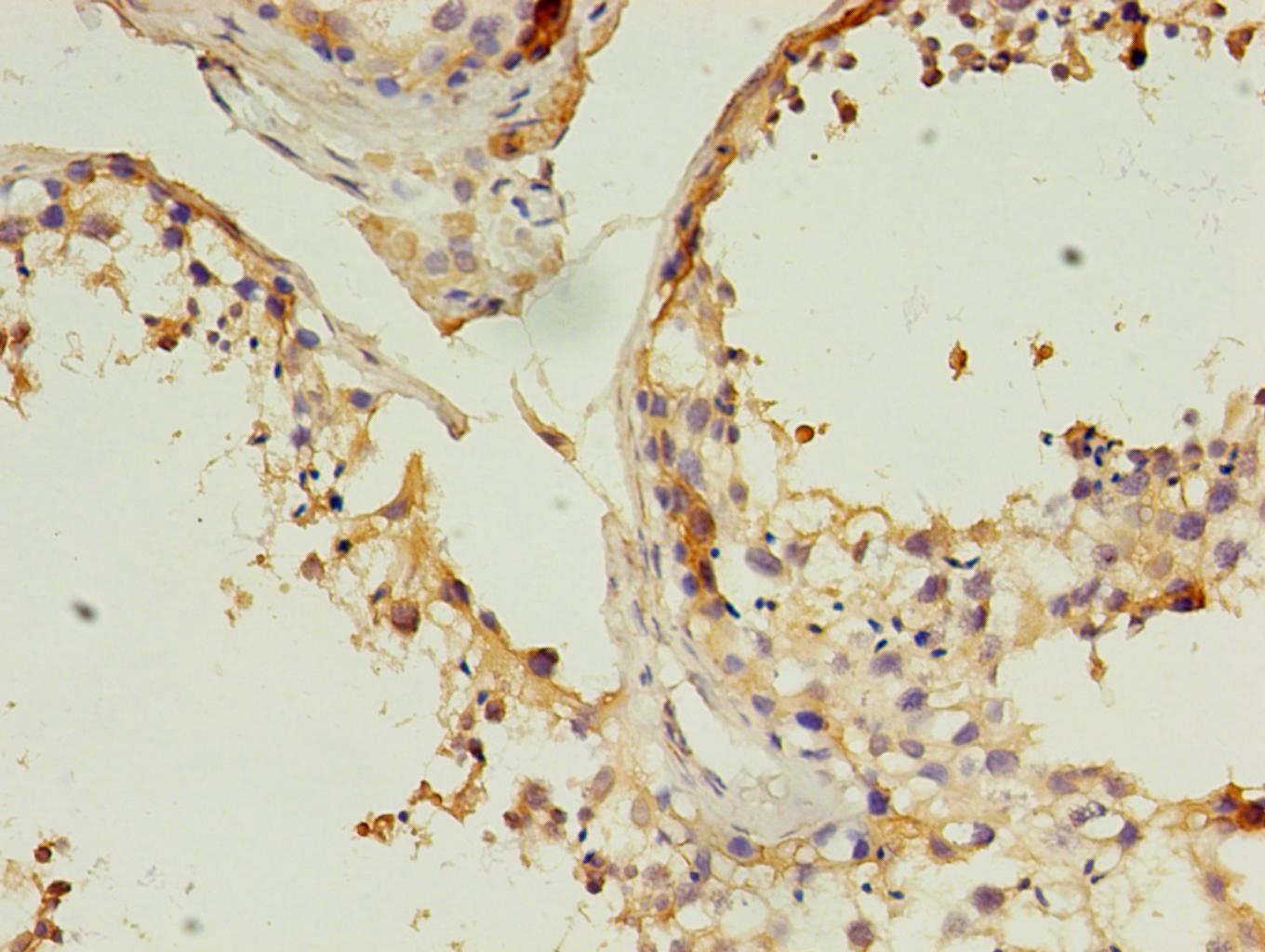
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung using #42017 in 30ug/ml dilute concentrations.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human testis using #42017 in 30ug/ml dilute concentrations. .
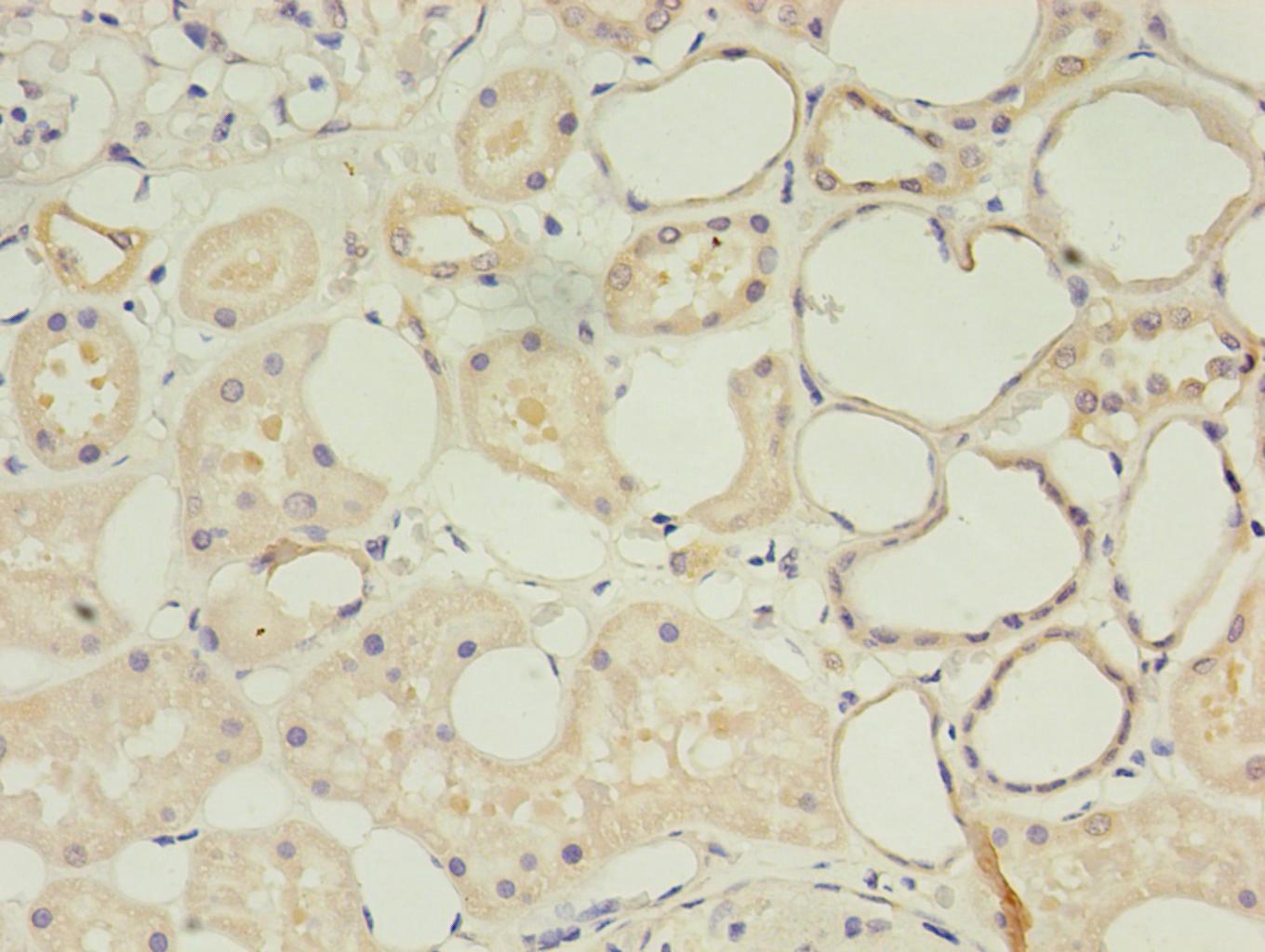
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human kidney using #42017 in 30ug/ml dilute concentrations.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung using #42017 in 30ug/ml dilute concentrations.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung using CSB-MA0048792A0m in 30ug/ml dilute concentrations.
As a component of the innate immune system, the cell surface glycoprotein CD14 is a myelomonocytic differentiation antigen preferentially expressed on monocytes, macrophages, and activated granulocytes. CD14 exists as two forms, either anchored into the membrane by a GPI-anchor tail (mCD14) or present as a soluble form (sCD14) in normal serum and body fluids. CD14 was first described as a pattern recognition receptor for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and a variety of ligands derived from different microbial sources, along with the co-receptors Toll-like receptor TLR 4 and MD-2. The binding of CD14 and LPS depends on the presence and catalytic activity of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP). Besides its endotoxin signaling function, CD14 has been proposed to be involved in various biological processes, including transportation of other lipids, cell-cell interaction during different immune responses, as well as recognition of apoptotic cells. Multiple transcript variants resulting from alternative splicing encode the same isoform of CD14.
If you have published an article using product 42017, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 The lead time is currently 1 week.
The lead time is currently 1 week.



