Product Detail
Product NameNF-H Antibody
Clone No.2G1
Host SpeciesMouse
ClonalityMonoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IP, IF, IHC(P)
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen DescA neurofilament NF-H protein isolated from a cytoskeletal preparation from brain tissue homogenate of calf origin.
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other Names200 kDa neurofilament protein antibody CMT2CC antibody Nefh antibody Neurofilament heavy polypeptide 200kDa antibody Neurofilament heavy polypeptide antibody Neurofilament triplet H protein antibody NF H antibody NF-H antibody NFH antibody NFH_HUMAN antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P12036
Uniprot
P12036
Gene ID
4744;
Calculated MW200 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:500-1:1000
IHC: 1:50-1:500
IP: 1-2 μg per 100-500 μg of total protein(1 ml of cell lysate)
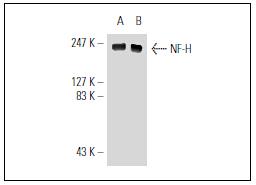
Western blot analysis of NF-H expression in rat brain (A) and mouse brain (B) tissue extracts.
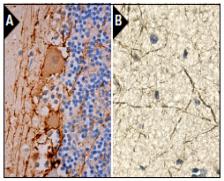
Immunoperoxidase staining of formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue showing membrane and cytoplasmic staining of Purkinje cells and neuropil staining in granular layer and molecular layer (A). Immunoperoxidase staining of formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue showing membrane and cytoplasmic staining of Purkinje cells and neuropil staining in granular layer and molecular layer (B).
Neurofilament-H (NF-H), for neurofilament heavy polypeptide, a member of the intermediate filament family, is a major component of neuronal cytoskeletons. Neurofilaments are dynamic structures; they contain phosphorylation sites for a large number of protein kinases, including protein kinase A, protein kinase C, cyclin-dependent kinase 5, extracellular signal regulated kinase, glycogen synthase kinase-3, and stress-activated protein kinase gamma. In addition to their role in the control of axon caliber, neurofilaments may affect other cytoskeletal elements, such as microtubules and Actin filaments. Changes in neurofilament phosphorylation or metabolism are frequently observed in neurodegenerative diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease.
If you have published an article using product 48320, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.


 Yes
Yes



