Product Detail
Product NameSerum Amyloid A (SAA) Antibody
Clone No.4G08
Host SpeciesMouse
ClonalityMonoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IP
Species ReactivityHu
Immunogen DescHighly purified recombinant SAA of human origin
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesAmyloid fibril protein AA antibody Amyloid fibrils antibody Amyloid protein A antibody Fibrils antibody MGC111216 antibody OC antibody PIG 4 antibody PIG4 antibody SAA 1 antibody SAA 2 antibody SAA antibody SAA_HUMAN antibody SAA1 antibody SAA2 antibody Serum amyloid A protein precursor antibody Serum amyloid A1 isoform 1 antibody Serum amyloid A1 isoform 2 antibody Serum amyloid protein A(4-101) antibody TP53I4 antibody Tumor protein p53 inducible protein 4 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot:P02735
Gene ID:6288
Uniprot
P0DJI8
Gene ID
6288;
Calculated MW12kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:100-1:1,000
IP: 1-2 μg per 100-500 μg of total protein(1 ml of cell lysate)
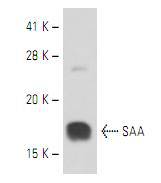
Western blot analysis of human recombinant SAA.
Western blot analysis of SAA expression in Caki-1 whole cell lysate (A) and of SAA human plasma (B).
The serum Amyloid A (SAA) family of proteins is encoded by muliple genes, which display allelic variation and a high degree of homology in mammals. The four members of the SAA gene family are clustered on human chromo- some 11p15.1. Three SAA genes are differentially expressed and encode small apolipoproteins. SAA1 and SAA2 encode the acute phase SAAs (A-SAAs) and SAA4 encodes the constitutively expressed SAA (C-SAA). A fourth locus, SAA3, is a pseudogene that contains two C/EBP-binding sites and a third site, which interacts with SAA3 enhancer factor . Human SAA proteins are a group of apolipoproteins found predominantly in the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) fraction of plasma. SAA is a major acute-phase protein and precursor to Amyloid A protein, which is the major constituent of the fibril deposits of reactive amyloidosis. SAA is secreted in large amounts by the liver during microbial infections or inflammatory diseases.
If you have published an article using product 48336, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes



