Product Detail
Product NameMSH6 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SP08-02
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF, IHC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesDNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 antibody G/T mismatch binding protein antibody G/T mismatch-binding protein antibody GTBP antibody GTMBP antibody hMSH6 antibody HNPCC 5 antibody HNPCC5 antibody HSAP antibody MSH 6 antibody MSH6 antibody MSH6_HUMAN antibody mutS (E. coli) homolog 6 antibody MutS alpha 160 kDa subunit antibody MutS homolog 6 (E. coli) antibody mutS homolog 6 antibody MutS-alpha 160 kDa subunit antibody p160 antibody Sperm associated protein antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P52701
Uniprot
P52701
Gene ID
2956;
Calculated MW153 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-5,000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
ICC: 1:50-1:200
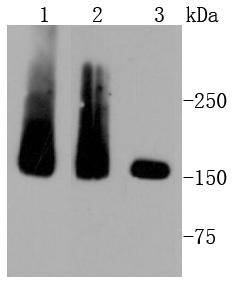
Western blot analysis of MSH6 on different lysates using anti-MSH6 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution. Positive control: Lane 1: HepG2 Lane 2: SW480 Lane 3: A549
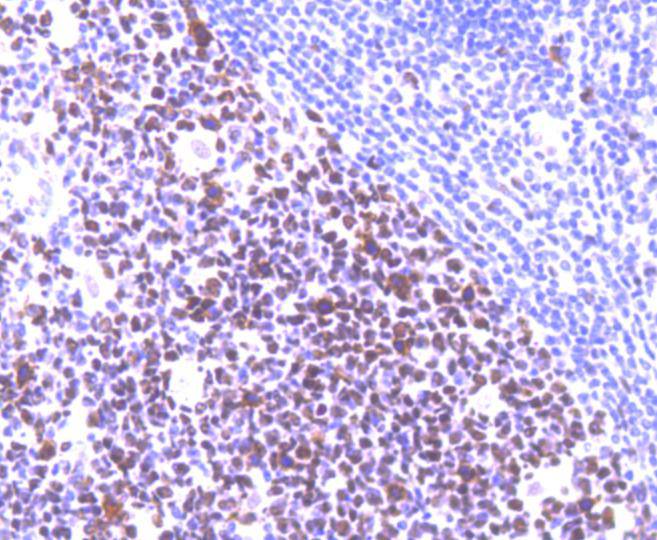
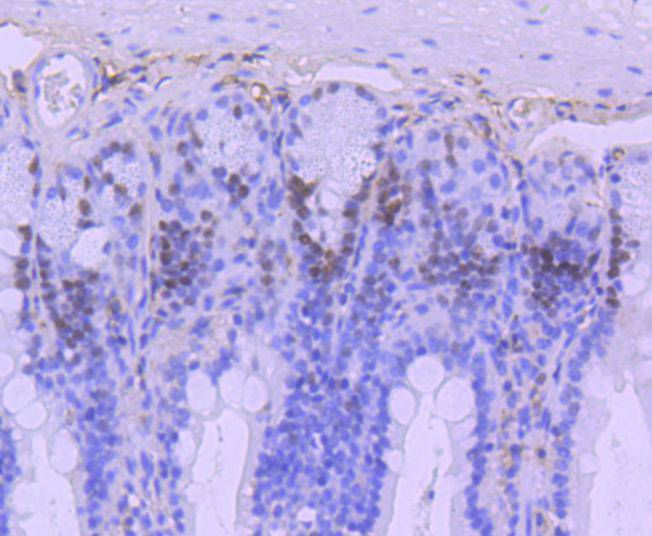
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue using anti-MSH6 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
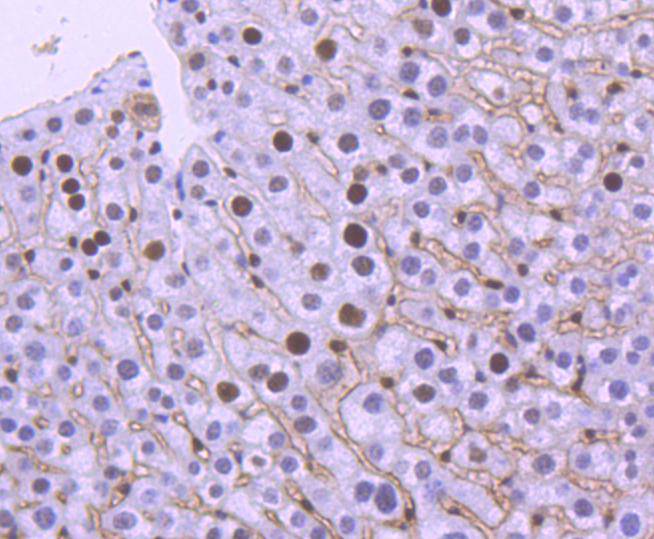
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse liver tissue using anti-MSH6 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
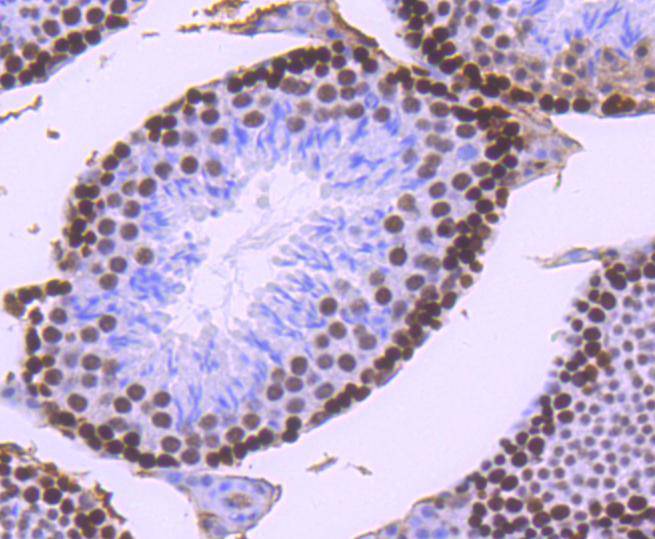
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse testis tissue using anti-MSH6 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse colon tissue using anti-MSH6 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
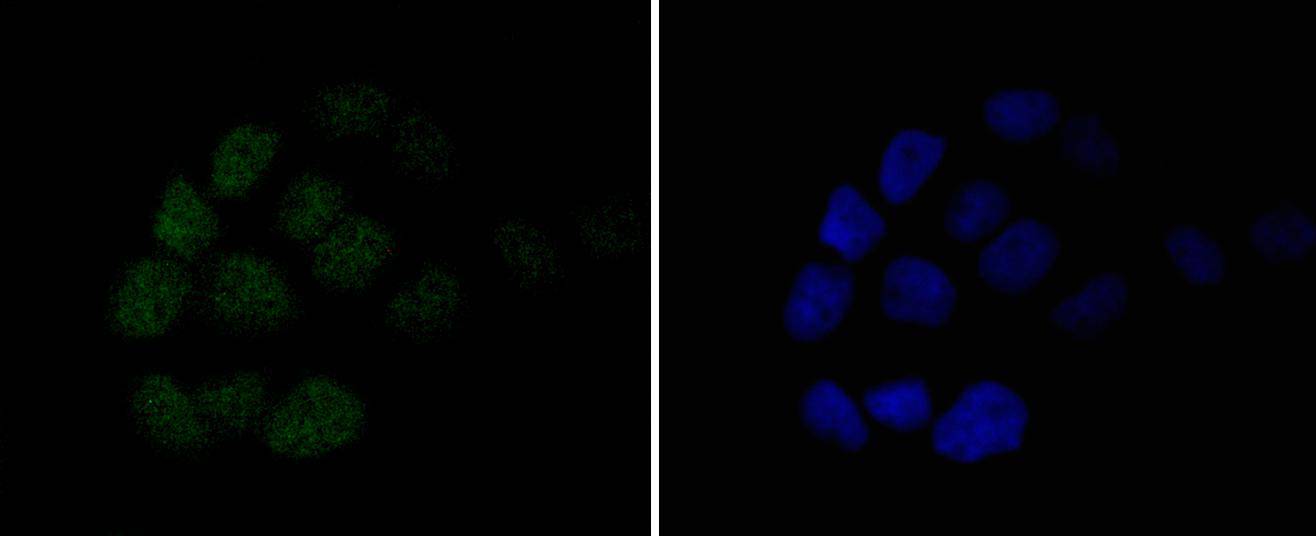
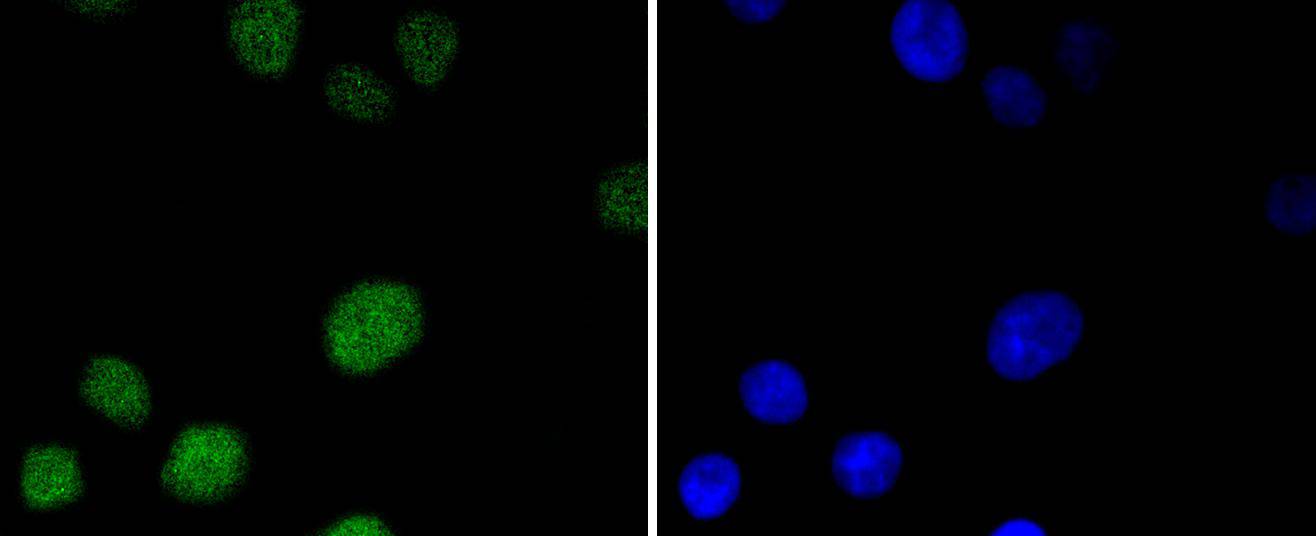
ICC staining MSH6 in A431 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
ICC staining MSH6 in A549 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
Multiple pathways promote short-sequence recombination (SSR) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. When gene conversion is initiated by a double-strand break (DSB), any nonhomologous DNA that may be present at the ends must be removed before new DNA synthesis can be initiated. Removal of a 3' nonhomologous tail in S. cerevisiae depends on the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease Rad1/Rad10 and also on the mismatch repair proteins Msh2 and Msh3. Msh2 and Msh3, which function in mitotic recombination, recognize not only heteroduplex loops and mismatched basepairs, but also branched DNA structures with a free 3' tail. Msh2 and Msh6 form a protein complex required to repair mismatches generated during DNA replication. Yeast Msh2-Msh6 interact asymmetrically with the DNA through base-specific stacking and hydrogen bonding interactions and backbone contacts. The importance of these contacts decreases with increasing distance from the mismatch, implying that interactions at or near the mismatch are important for binding in a kinked DNA conformation.
If you have published an article using product 48711, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.


 Yes
Yes



