Product Detail
Product NameHDAC1 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SY12-04
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF, IHC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesDKFZp686H12203 antibody GON 10 antibody HD1 antibody HDAC 1 antibody HDAC1 antibody HDAC1_HUMAN antibody Histone deacetylase 1 antibody Reduced potassium dependency yeast homolog like 1 antibody RPD3 antibody RPD3L1 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:Q13547
Uniprot
Q13547
Gene ID
3065;
Calculated MW65 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-1:2,000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
ICC: 1:50-1:200
FC: 1:50-1:100
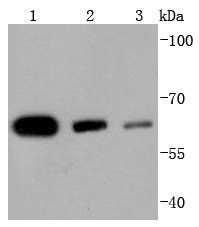
Western blot analysis of HDAC1 on different lysates using anti-HDAC1 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution. Positive control: Lane 1: Hela Lane 2: Jurkat Lane 3: K562
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue using anti-HDAC1 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse colon tissue using anti-HDAC1 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
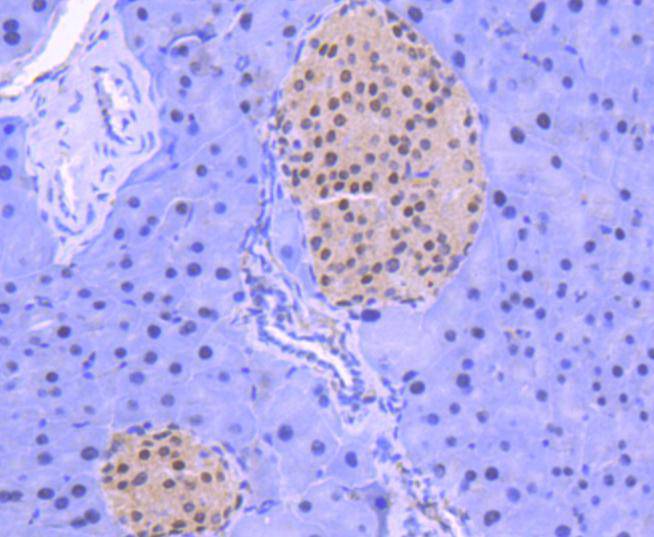
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse pancreas tissue using anti-HDAC1 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Acetylation of the histone tail causes chromatin to adopt an "open" conformation, allowing increased accessibility of transcription factors to DNA. The identification of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and their large multiprotein complexes has yielded important insights into how these enzymes regulate transcription. HAT complexes interact with sequence-specific activator proteins to target specific genes. In addition to histones, HATs can acetylate nonhistone proteins, suggesting multiple roles for these enzymes. In contrast, histone deacetylation promotes a "closed" chromatin conformation and typically leads to repression of gene activity. Mammalian histone deacetylases can be divided into three classes on the basis of their similarity to various yeast deacetylases. Class I proteins (HDACs 1, 2, 3, and 8) are related to the yeast Rpd3-like proteins, those in class II (HDACs 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10) are related to yeast Hda1-like proteins, and class III proteins are related to the yeast protein Sir2. Inhibitors of HDAC activity are now being explored as potential therapeutic cancer agents.
If you have published an article using product 48727, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.




 Yes
Yes



