Product Detail
Product Name14-3-3 gamma Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SD20-65
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, FC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other Names14 3 3 gamma antibody
14 3 3 protein gamma antibody
14 3 3 protein gamma subtype antibody
14 3 3gamma antibody
14-3-3 protein gamma antibody
1433G_HUMAN antibody
3 monooxygenase/tryptophan 5 monooxgenase activation protein gamma polypeptide antibody
KCIP 1 antibody
KCIP-1 antibody
KCIP1 antibody
N-terminally processed antibody
Protein kinase C inhibitor protein 1 antibody
Tyrosine 3 monooxygenase/tryptophan 5 monooxygenase activation protein gamma polypeptide antibody
Ywhag antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P61981
Uniprot
P61981
Gene ID
7532;
Calculated MW28 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-1:2,000
FC: 1:10-1:50
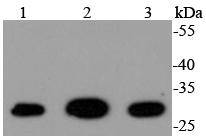
Western blot analysis of 14-3-3 gamma on different lysates using anti-14-3-3 gamma antibody at 1/1,000 dilution. Positive control: Lane 1: 293T Lane 2: A431 Lane 3: Hela
Flow cytometric analysis of K562 cells with 14-3-3 gamma antibody at 1/50 dilution (red) compared with an unlabelled control (cells without incubation with primary antibody; black). Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti rabbit IgG was used as the sec�?��?��?�?��?��c���
14-3-3 proteins regulate many cellular processes relevant to cancer biology, notably apoptosis, mitogenic signaling and cell-cycle checkpoints. Seven isoforms comprise this family of signaling intermediates, denoted 14-3-3 b, g, e, z, h, q and s. 14-3-3 proteins form dimers that present two binding sites for ligand proteins, thereby bringing together two proteins that may not otherwise associate. These ligands largely share a 14-3-3 consensus binding motif and exhibit serine/threonine phosphorylation. 14-3-3 proteins function in broad regulation of these ligand proteins; by cytoplasmic sequestration, occupation of interaction domains and import/export sequences, prevention of degradation, activation/repression of enzymatic activity, and facilitation of protein modification. Loss of expression contributes to a vast array of pathogenic cellular activities.
If you have published an article using product 49205, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes



