Product Detail
Product NameGLUT2 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.JJ20-21
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IHC, FC
Species ReactivityHu
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other Namesliver antibody Glucose Transporter 2 antibody Glucose Transporter GLUT2 antibody Glucose transporter type 2 antibody Glucose transporter type 2 liver antibody Glucose transporter, liver/islet antibody GLUT-2 antibody GLUT2 antibody GTR2_HUMAN antibody GTT2 antibody SLC2A2 antibody Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter) member 2 antibody Solute carrier family 2 facilitated glucose transporter member 2 antibody Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 2 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P11168
Uniprot
P11168
Gene ID
6514;
Calculated MW57 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:500-1:1000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
FC: 1:50-1:100
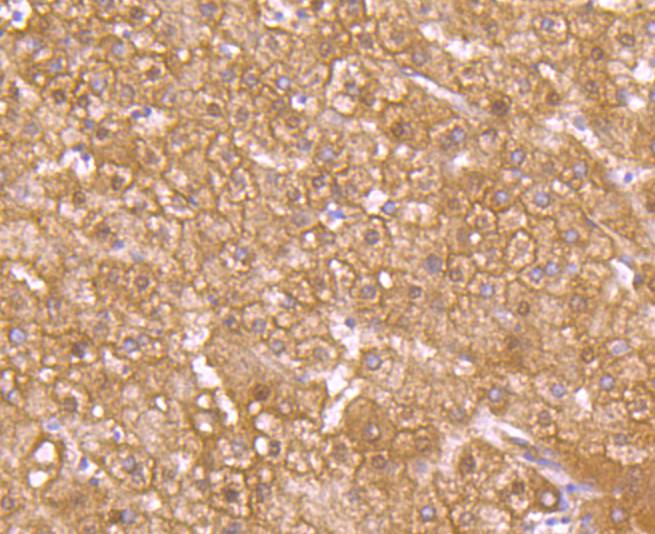
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver tissue using anti-GLUT2 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
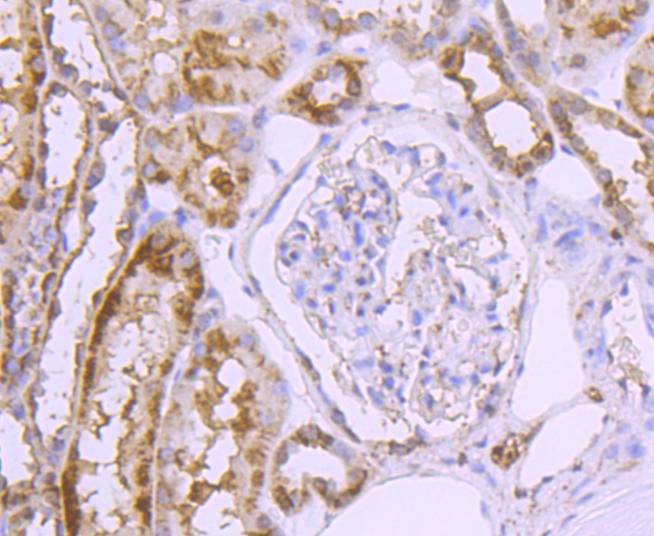
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human kideny tissue using anti-GLUT2 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
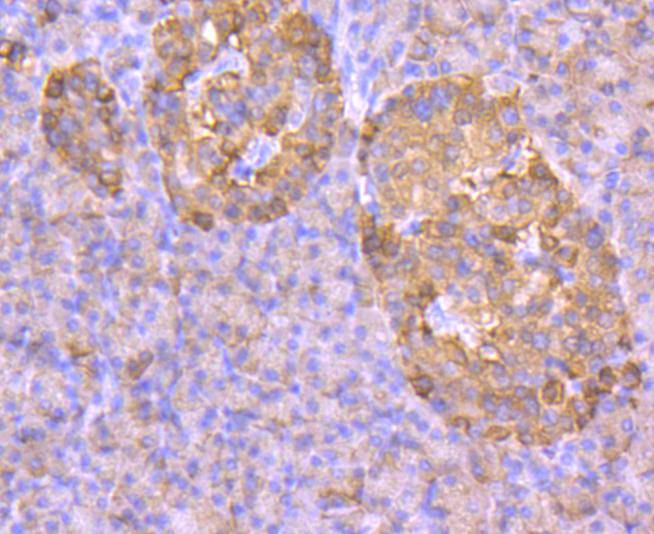
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human pancreas tissue using anti-GLUT2 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
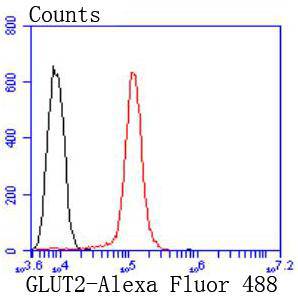
Flow cytometric analysis of HepG2 cells with GLUT2 antibody at 1/50 dilution (red) compared with an unlabelled control (cells without incubation with primary antibody; black). Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti rabbit IgG was used as the secondary antibody
Glucose is fundamental to the metabolism of mammalian cells. Its passage across cell membranes is mediated by a family of transporters termed glucose transporters or Gluts. Glut1, Glut3 and Glut4 are high-affinity transporters, whereas Glut2 is a low-affinity transporter. In adipose and muscle tissue, insulin stimulates a rapid and dramatic increase in glucose uptake, which is largely due to the redistribution of the insulin-inducible glucose transporter Glut4. In response to insulin, Glut4 is quickly shuttled from an intracellular storage site to the plasma membrane, where it binds glucose. In contrast, the ubiquitously expressed glucose transporter Glut1 is constitutively targeted to the plasma membrane and shows a much less dramatic translocation in response to insulin. Glut2 expression is seen in pancreatic beta cells, hepatocytes and basolateral membranes of intestinal and epithelial cells, while the highest expression of Glut3 has been found in neuronal tissue.
If you have published an article using product 49243, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.


 Yes
Yes



