Product Detail
Product NameBag3 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.JA90-53
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IHC, IP
Species ReactivityHu
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesBAG 3 antibody
BAG family molecular chaperone regulator 3 antibody
BAG-3 antibody
Bag3 antibody
BAG3_HUMAN antibody
Bcl 2 binding protein antibody
Bcl-2-associated athanogene 3 antibody
Bcl-2-binding protein Bis antibody
BCL2 associated athanogene 3 antibody
BCL2 binding athanogene 3 antibody
BIS antibody
CAIR 1 antibody
Docking protein CAIR 1 antibody
Docking protein CAIR-1 antibody
MFM6 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:O95817
Uniprot
O95817
Gene ID
9531;
Calculated MW75 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-1:2,000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
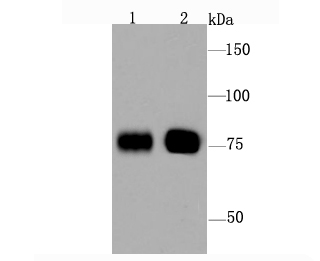
Western blot analysis of Bag3 on Hela (1) and MCF-7 (2) cell using anti-Bag3 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
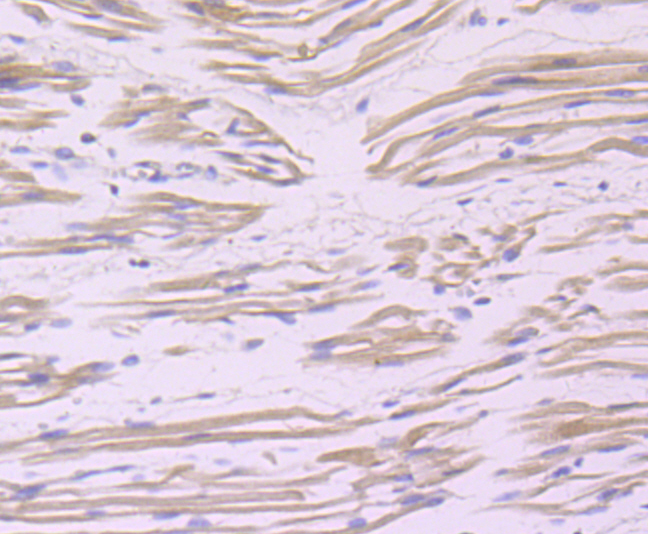
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human fetal skeletal muscle tissue using anti-Bag3 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
The Bag family of proteins are characterized by the presence of a 45 amino acid Bag domain through which they bind with high affinity to the ATPase domain of HSP 70, thereby negatively regulating HSP 70 chaperone activity. Bag-3 (Bcl-2-associated athanogene 3), also known as BIS or CAIR-1, is a 575 amino acid protein that contains one C-terminal Bag domain and two N-terminal WW domains. Like other members of the Bag family, Bag-3 functions to inhibit the chaperone activity of HSP 70, specifically by promoting the release of HSP 70-bound substrates. Additionally, Bag-3 exhibits anti-apoptotic activity via cell cycle control, suggesting a possible role for Bag-3 in tumor progression. The gene encoding Bag-3 maps to human chromosome 10, which houses over 1,200 genes and comprises nearly 4.5% of the human genome.
If you have published an article using product 49578, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.


 Yes
Yes



