Product Detail
Product Namec Met (Phospho-Tyr1349) Rabbit mAb
Clone No.S05-3D6
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
ClonalityMonoclonal
IsotypeIgG
PurificationAffinity Purified
ApplicationsWB,IHC
Species ReactivityHuman
Immunogen DescA synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Tyr1349 of human Met
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesHGFR; AUTS9; RCCP2; c-Met; DFNB97
Accession NoSwiss-Prot:P08581
GeneID:4233
Uniprot
P08581
Gene ID
4233
Calculated MWPredicted band size: 156 kDa
Sdspage MWObserved band size: 140kDa
Concentration0.3 mg/ml
FormulationRabbit IgG in 10mM phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
StorageStore at 4˚C short term. Aliquot and store at -20˚C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Application Details
WB: 1:500-1:2000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
All lanes : c Met (Phospho-Tyr1349) Rabbit mAb at 1/1k dilutionLane 1 : Hela whole cell lysatesLane 2 : Hela treated with 40 ng/ml HGF for 5 min whole cell lysatesLysates/proteins at 20 µg per lane.SecondaryAll lanes : Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) at 1/20000 dilutionPredicted band size: 156 kDa Observed band size: 140kDaExposure time: 5 seconds
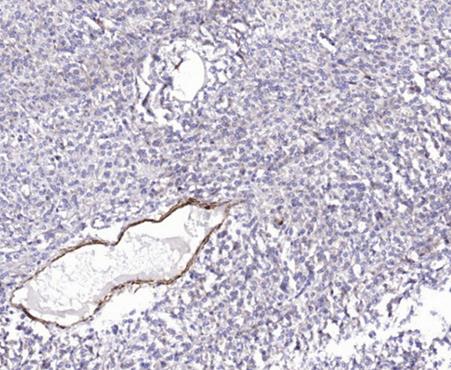
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human colon cancer tissue stained for Phospho-c Met (Tyr1349) using 52699 at 1/100 dilution in immunohistochemical analysis.
This gene encodes a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family of proteins and the product of the proto-oncogene MET. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate alpha and beta subunits that are linked via disulfide bonds to form the mature receptor. Further processing of the beta subunit results in the formation of the M10 peptide, which has been shown to reduce lung fibrosis. Binding of its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor, induces dimerization and activation of the receptor, which plays a role in cellular survival, embryogenesis, and cellular migration and invasion. Mutations in this gene are associated with papillary renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and various head and neck cancers. Amplification and overexpression of this gene are also associated with multiple human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]
If you have published an article using product 52699, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes



