Product Detail
Product NameHuman P-selectin ELISA kit
ApplicationsELISA
Species ReactivityHu
SpecificityNatural and recombinant Human P-selectin Ligand
Target NameHuman P-selectin
Application Details
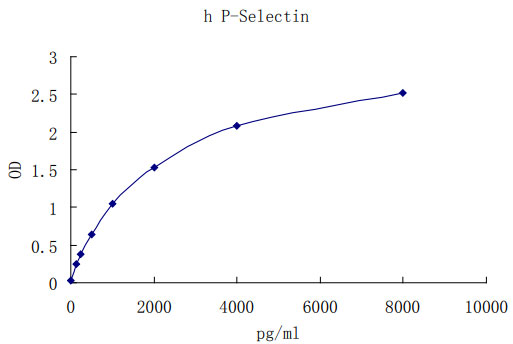
Detect Range: 125-8000pg/ml
Sensitivity: 62pg/mL
Sample Type: Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
Sample Volume: 20 uL
Assay Time: 3 hours
Detection method: Colorimetric
P-Selectin (GMP-140, LECAM-3, PADGEM, CD62, CD62P) is a cell surface glycoprotein that plays a critical role in the migration of lymphocytes into tissues (1 - 5). It is found constitutively in a pre-formed state in the Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells and in the alpha granules of platelets (4). This stored P-Selectin is mobilized to the cell surface within minutes in response to a variety of inflammatory or thrombogenic agents (4). The mobilized P-Selectin is apparently present on the cell surface for only a few minutes after which it is recycled to intracellular compartments (4). Additional evidence indicates that transcription of P-Selectin mRNA can be activated in the endothelium by treatment with inflammatory mediators (6).
P-Selectin consists of an NH2-terminal lectin type C domain, an EGF-like domain, nine complement control domains, a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic domain (1,2). Mouse P-Selectin shows a similar organization of functional domains and an overall sequence identity of approximately 73% (5, 6). However, mouse P-Selectin contains only eight
complement control domains, suggesting that the absolute number of these domains is not crucial for function (6). The molecular weight predicted from the cDNA for P-Selectin is approximately 86,000 (1, 2). The observed molecular weight on reducing SDS-PAGE,however, is approximately 140,000 (2).
Evidence indicates that P-Selectin is involved in the adhesion of myeloid cells, as well as B cells and a subset of T cells, to activated endothelium (4). P-Selectin is also involved in the adhesion of platelets to monocytes and neutrophils, playing a central role in neutrophil accumulation within thrombi (4). The adhesion of leukocytes and neutrophils to the endothelium is initiated by weak interactions that produce a characteristic


 YES
YES



