Product Detail
Product NameMouse MIP-2 ELISA kit
ApplicationsELISA
Species ReactivityMs
SpecificityNatural and recombinant Mouse MIP-2 Ligand
Target NameMouse MIP-2
Application Details
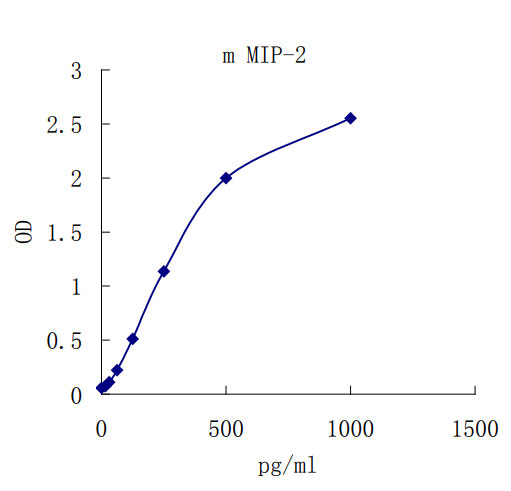
Detect Range: 0.02 - 1.0 ng/mL
Sensitivity: 7pg/mL
Sample Type: Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
Sample Volume: 20 uL
Assay Time: 3 hour
Detection method: Colorimetric
Mouse macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), also known as CXCL2, was originally identified as a heparin-binding protein secreted by an LPS-stimulated mouse macrophage cell line (1). A cDNA clone encoding the protein was isolated from this cell line and characterized (2). Based on its protein and DNA sequences, mouse MIP-2 was classified as a member of the alpha (CXC) chemokine family of inflammatory and immunoregulatory cytokines (3).
Mouse MIP-2 cDNA encodes a 100 amino acid residue precursor protein from which the amino-terminal 27 amino acid residues are cleaved to generate the mature mouse MIP-2. The protein sequence of mouse MIP-2 shows approximately 63% identity to that of mouse KC, another mouse alpha chemokine. Mouse MIP-2 is also 60% identical to human GROβ and GROγ(2). Based on these protein sequence similarities, it is likely that mouse KC and MIP-2 are homologs of human GROα, β and γ chemokines. Since chemokines with protein sequence homology to human IL-8 have not been identified in mice, it has been suggested that the mouse KC and MIP-2 are functional homologs of human IL-8 in mice (3, 4). A putative mouse homolog of the human IL-8 receptor beta (IL-8 Rβ) has also been cloned. This receptor shows 71% identity to human IL-8 Rβ and 68% identity to human IL-8 Rα. Both mouse KC and MIP-2 bind mouse IL-8 Rβ with high affinity (5).
Like human IL-8, mouse MIP-2 exhibits potent neutrophil chemotactic activity and may be a key mediator of neutrophil recruitment in response to tissue injury and infection (3, 4). Increased MIP-2 expression has been found to be associated with neutrophil influx in various inflammatory conditions (6 - 10).
If you have published an article using product EK0504, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.
et al,Abietic acid attenuates sepsis-induced lung injury by inhibiting NF-kB pathway to inhibit M1 macrophage polarization. In Exp Anim
on 2022 Nov 10 by Honglong Fang, Juan Chen, et al..PMID:35644586
, (2022),
PMID:
35644586


 YES
YES



