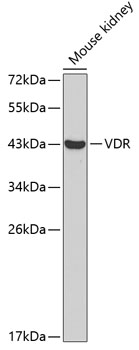
The vitamin D receptor (VDR), also known as the calcitriol receptor, and also known as NR1I1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 1), is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Upon activation by vitamin D, the VDR forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor and binds to hormone response elements on DNA resulting in expression or trans-repression of specific gene products.It is an intracellular hormone receptor that specifically binds 1,25(OH)2D3 and mediates its effects. Downstream targets of this nuclear hormone receptor are principally involved in mineral metabolism though the receptor regulates a variety of other metabolic pathways, such as those involved in the immune response and cancer. Defects in VDR are the cause of rickets vitamin D-dependent type 2A (VDDR2A). A disorder of vitamin D metabolism results in severe rickets, hypocalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Most patients have total alopecia in addition to rickets. This antibody is a rabbit Primary antibodyto human VDR.