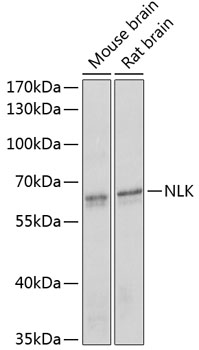
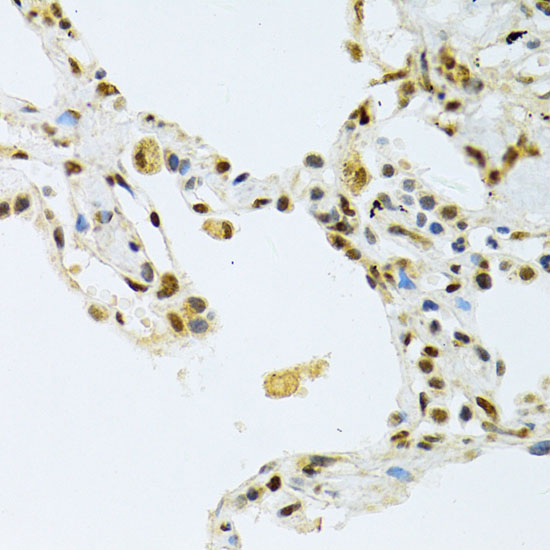
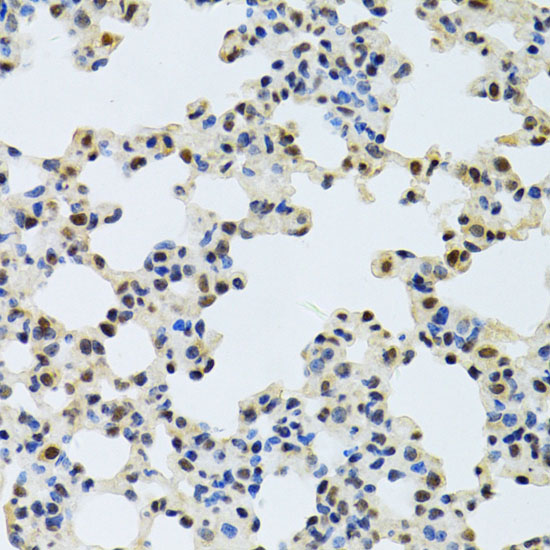
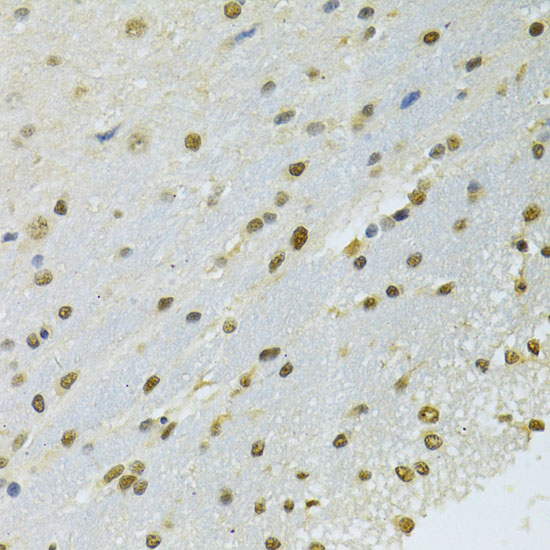
The activation of signal transduction pathways by growth factors, hormones and neurotransmitters is mediated through two closely related MAP kinases, p44 and p42, designated extracellular-signal related kinase 1 (ERK 1) and ERK 2, respectively. ERK proteins are regulated by dual phosphorylation at specific tyrosine and threonine sites mapping within a characteristic Thr-Glu-Tyr motif. Phosphorylation at both Thr-183 and Tyr-185 is required for full enzymatic activation. In response to activation, MAP kinases phosphorylate downstream components on serine and threonine (5,6). Nlk, or nemo-like kinase, is a murine homolog of the Drosophila nemo (nmo) gene. Nlk and Nmo have sequence homology to both the ERK MAP kinases and the cyclin dependent kinases. Nlk is a nuclear protein with the ability to autophosphorylate.