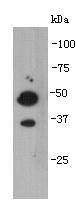
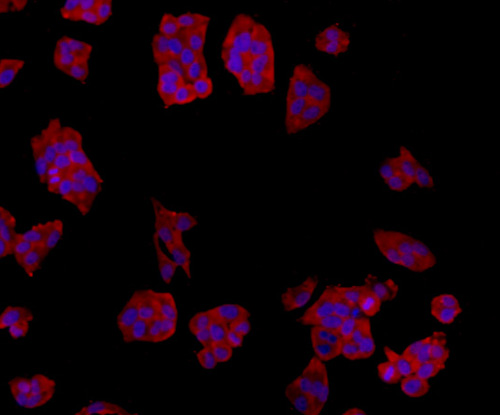
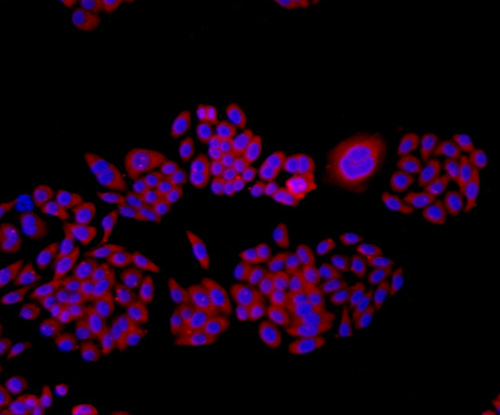
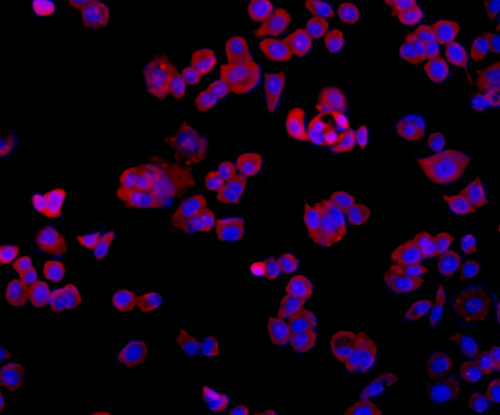
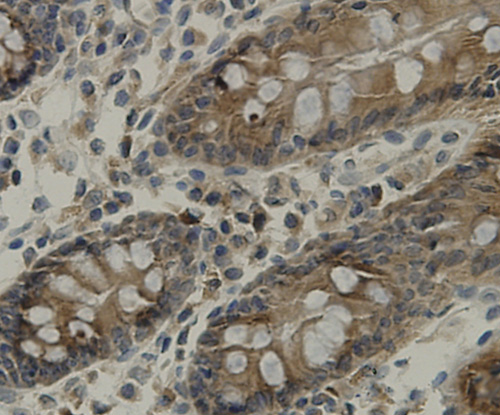
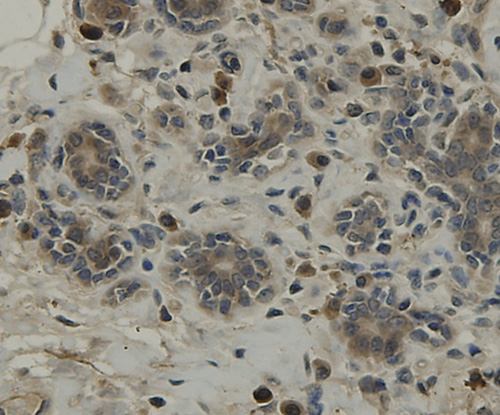
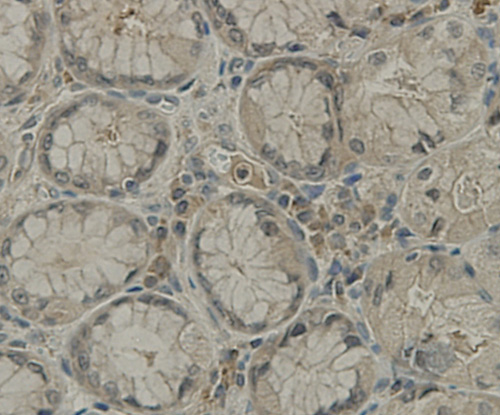
A transmembrane protein (TMEM) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the biological membrane to which it is permanently attached. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the biological membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. Transmembrane proteins are polytopic proteins that aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.