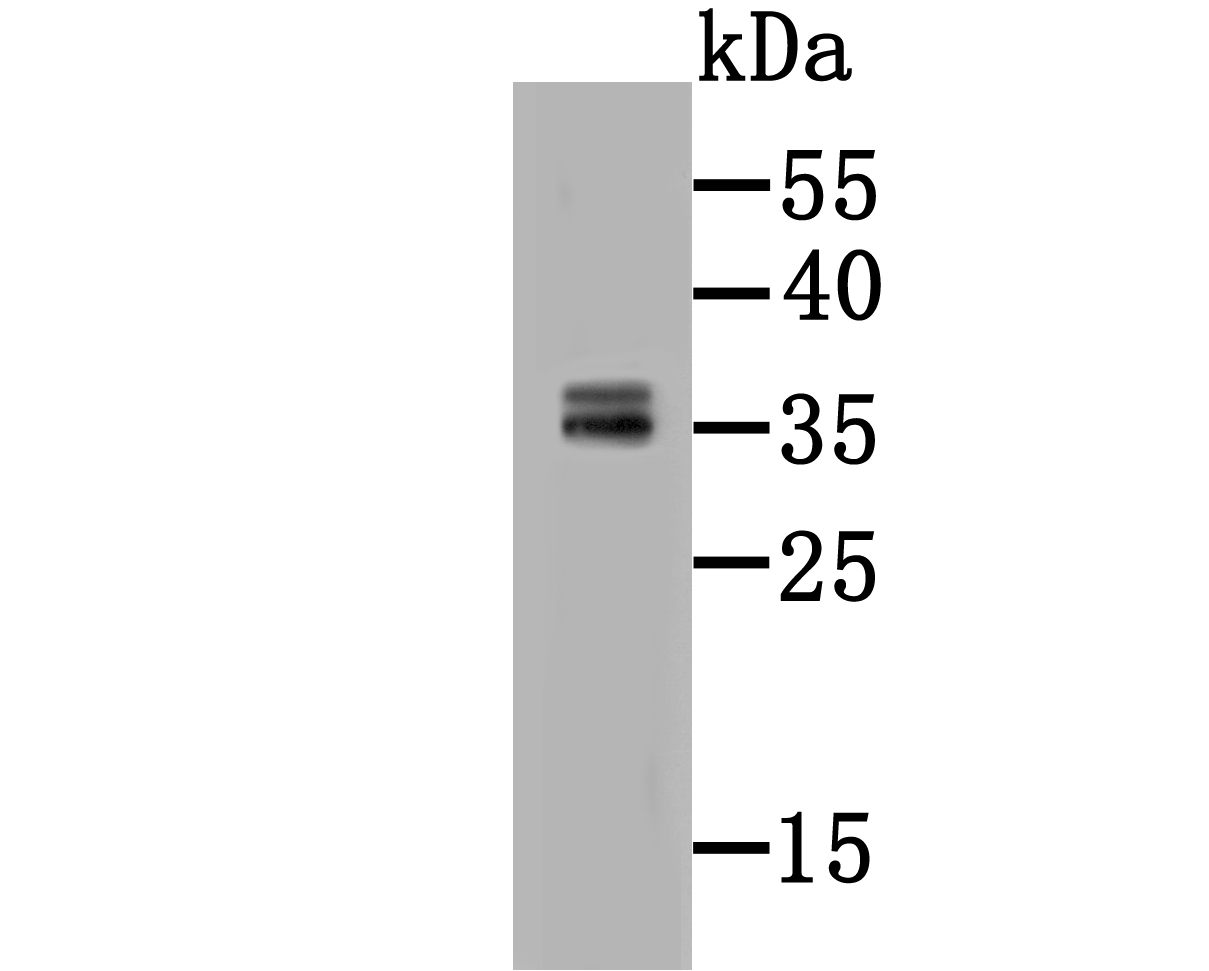
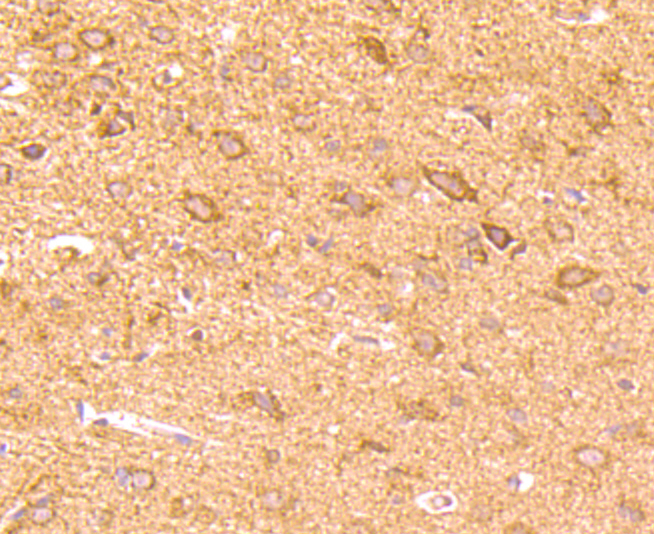
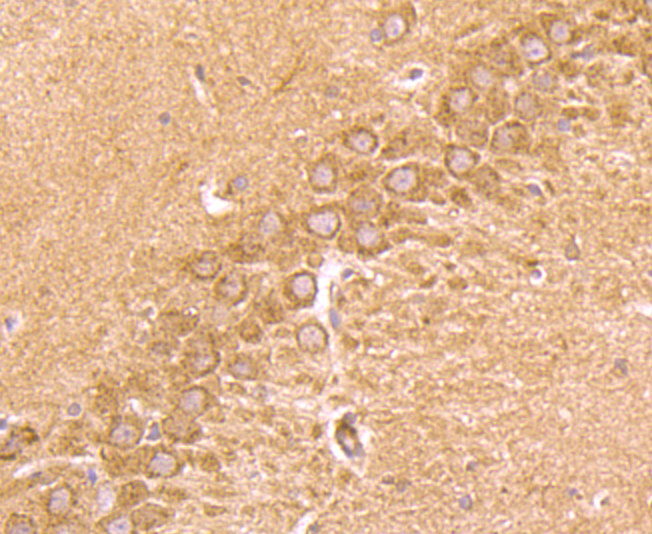
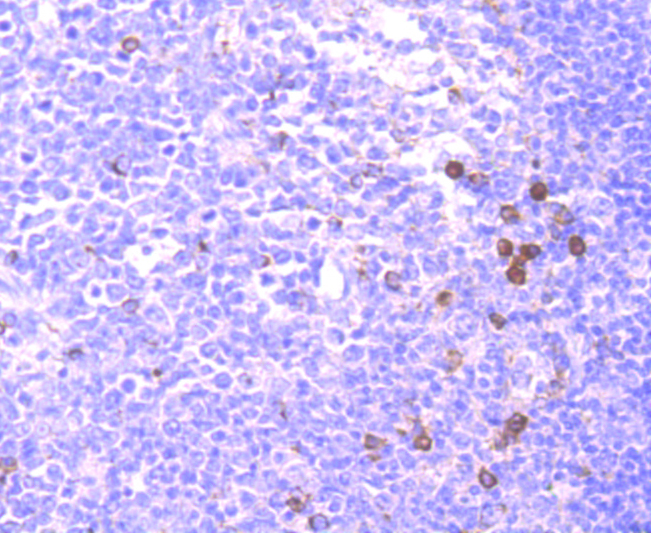
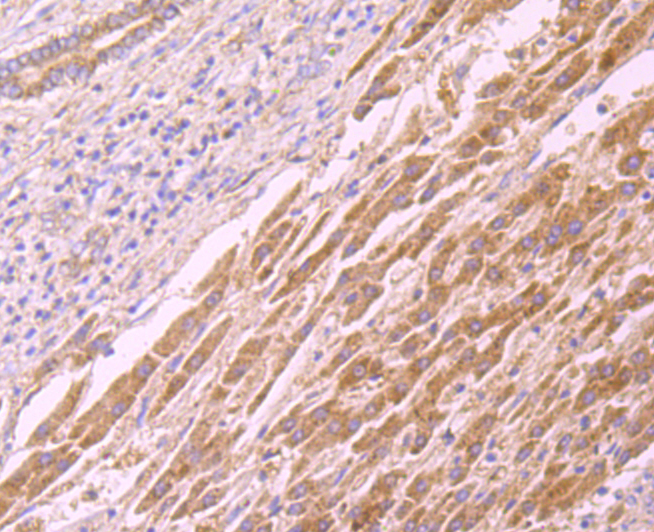
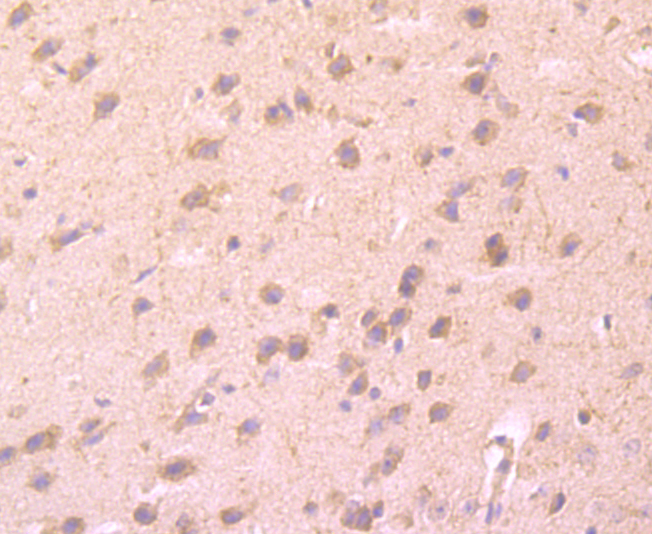
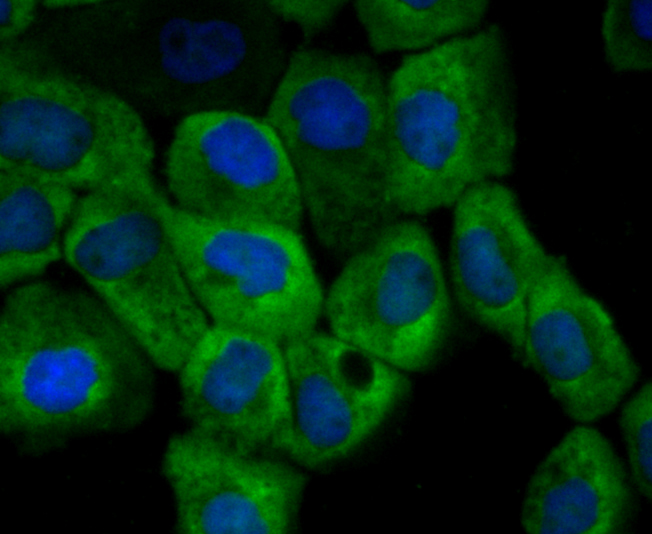
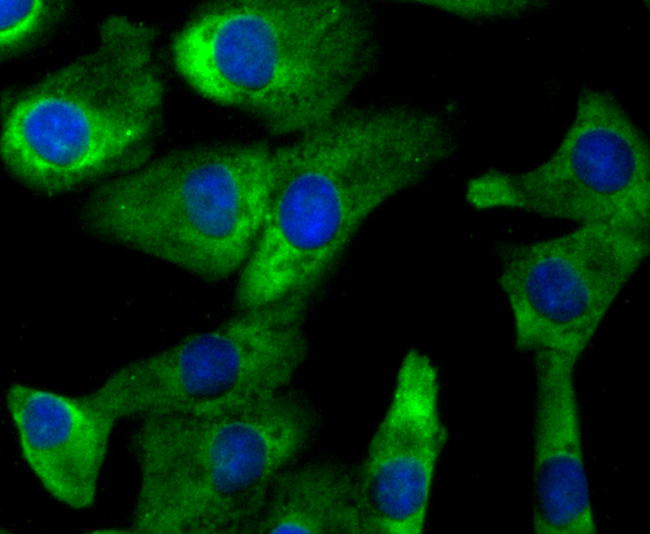
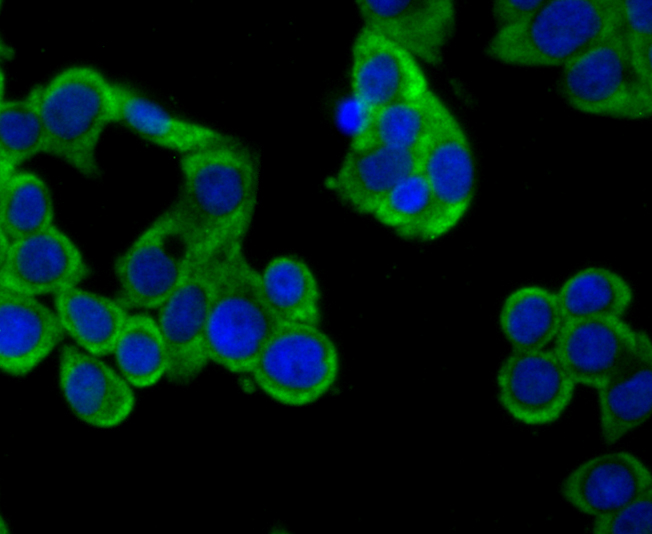
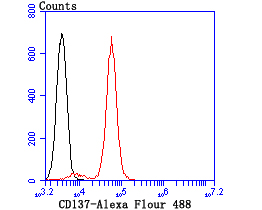
CD137, also designated ILA and 4-1BB in mouse, belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor family and delivers a costimulatory signal to T lymphocytes. CD137 is expressed on activated T cells and binds an inducible ligand that is found on B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Interactions between CD137 and its ligand are involved in antigen presentation and the generation of cytotoxic T cells. Crosslinking of the CD137 ligand induces apoptosis in resting lymphocytes. In contrast, CD137 regulates peripheral monocyte survival by inducing a cytokine release profile, and is mediated by M-CSF and to a lesser extent by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-3. Soluble forms of CD137 are found in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and may provide a negative control mechanism for immune responses.