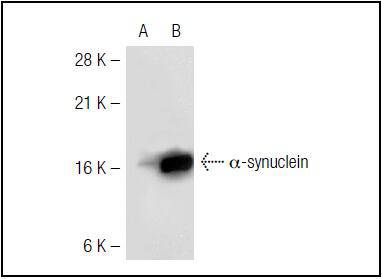
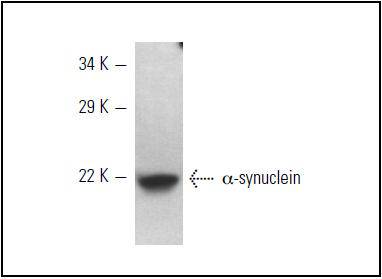
The synuclein family members, including ?-synuclein (also designated NACP for non--Amyloid component) and -synuclein, are predominantly expressed in the brain and are speculated to be involved in synaptic regulation and neuronal plasticity. ?-synuclein is localized to neuronal cell bodies and synapses. ?-synuclein was first identified as a component of Alzheimers disease amyloid plaques. Abnormal platelet function in Alzheimers disease has been demonstrated. During megakaryocytic differentiation ?-synuclein has been found to be upregulated, while -synuclein is downregulated, indicating that coordinate expression of synucleins may be important during hematopoetic cell differentiation. A mutant form of ?-synuclein has been found in patients with early onset Parkinsons disease.