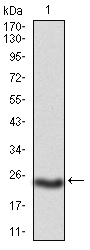
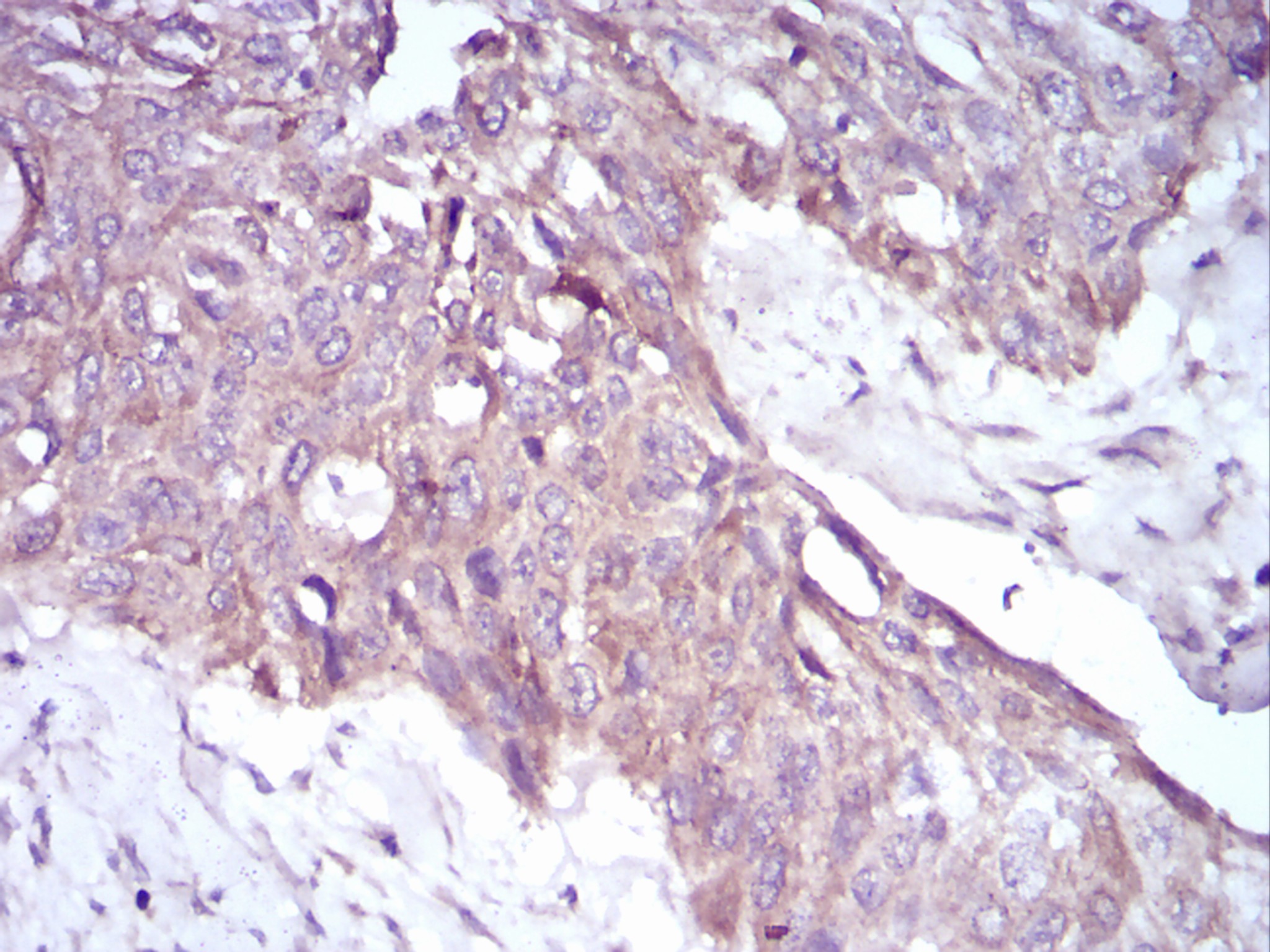
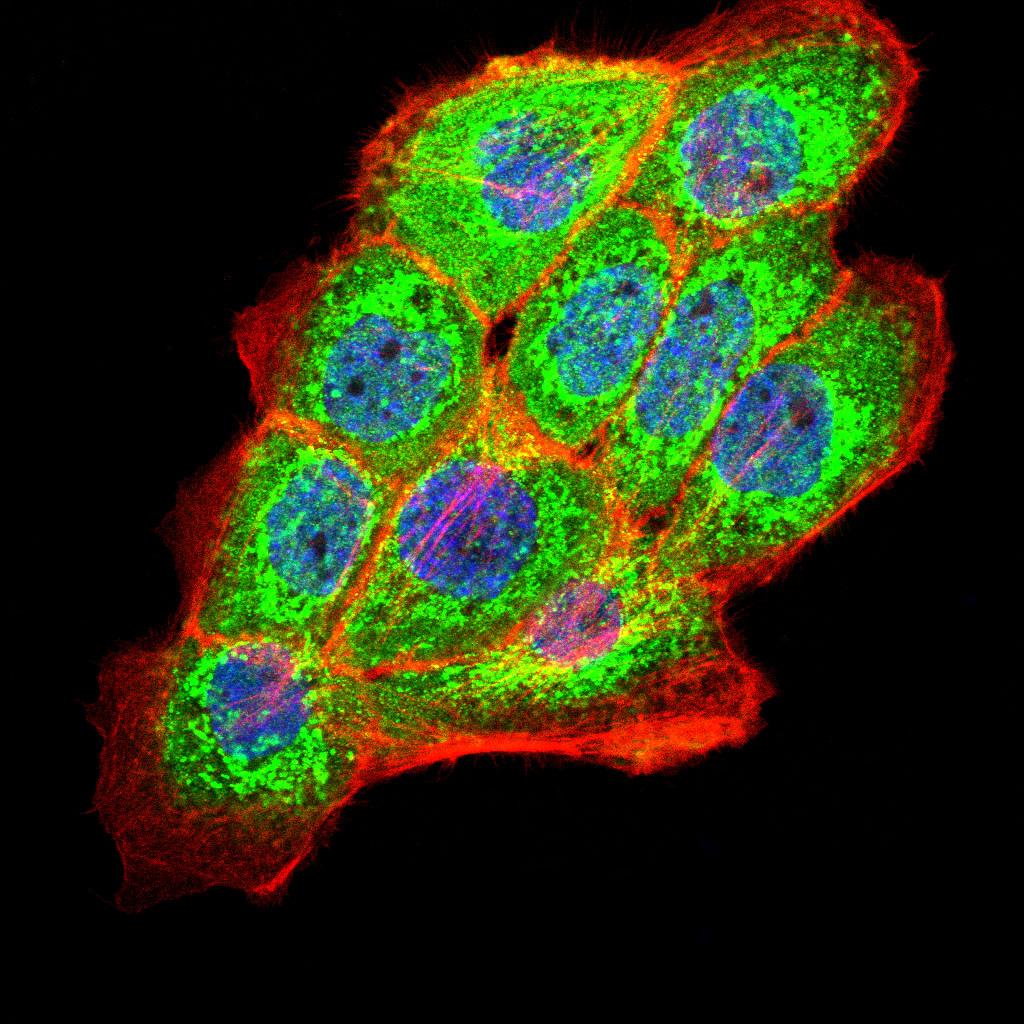
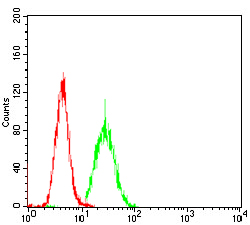
May be required for correct bipolar cell division through the regulation of centrosome duplication and mitotic spindle assembly. May be a receptor protein that acts in collecting-duct and biliary differentiation. Defects in PKHD1 are the cause of polycystic kidney disease autosomal recessive (ARPKD). ARPKD is a severe form of polycystic kidney disease affecting the kidneys and the hepatic biliary tract. The clinical spectrum is widely variable, with most cases presenting during infancy. The fetal phenotypic features classically include enlarged and echogenic kidneys, as well as oligohydramnios secondary to a poor urine output. Up to 50% of the affected neonates die shortly after birth, as a result of severe pulmonary hypoplasia and secondary respiratory insufficiency. In the subset that survives the perinatal period, morbidity and mortality are mainly related to severe systemic hypertension, renal insufficiency, and portal hypertension due to portal-tract fibrosis.