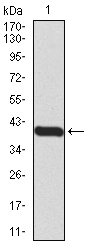
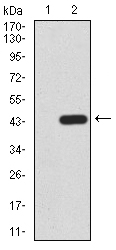
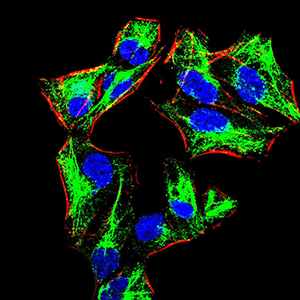
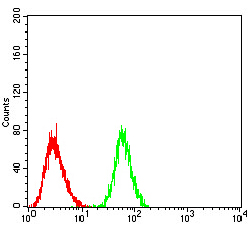
The development and differentiation of plasma cells, which are terminally differentiated B-cells, are induced by Blimp-1 (B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein, also designated PRDI-BF1). Blimp-1 is a transcriptional repressor that localizes to the nucleus and is considered a master regulator of terminal B-cell development. Alone, Blimp-1 is sufficient to trigger terminal B-cell differentiation. Blimp-1 upregulates the expression of syndecan-1 and J chain, represses IFN-b gene transcription and associates with HDAC to recruit it to DNA, thereby repressing c-myc. Blimp-1 is expressed during the late stages of B-cell differentiation in immunoglobulin-secreting plasma cells, as well as in long-lived, bone marrow plasma cells. The expression of Blimp-1 defines a checkpoint beyond which fully activated B cells proceed to the plasma cell stage, whereas immature and partially activated cells are eliminated.