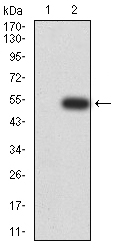
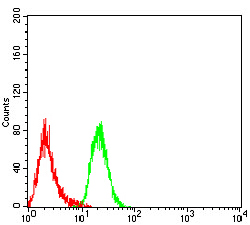
Helicases are enzymes that catalyze the separation of double stranded DNA or RNA by utilizing ATP. LGP2, also known as probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DHX58, is a 678 amino acid protein belonging to the helicase family. LGP2 acts as a negative regulator of host innate immune defense against viruses by binding dsRNA produced during viral replication. The repressor domain of LGP2 binds to RIG-I, a signaling protein involved in host defenses against hepatitis C virus (HCV). By preventing RIG-I multimerization, LGP2 negatively regulates RIG-I-mediated signaling. Localized to the cytoplasm, LGP2 contains one helicase ATP-binding domain and one helicase C-terminal domain.