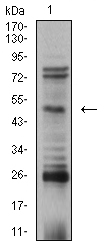
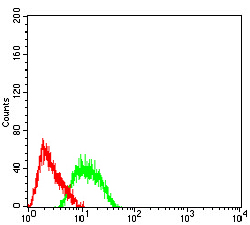
AP-2 transcription factor family members include AP-2α, AP-2β and AP-2γ, which specifically bind to the DNA consensus sequence CCCCAGGC and initiate transcription of selected genes. AP-2, also known as ERF-1, plays a role in regulating estrogen receptor expression. AP-2β, a splice variant of AP-2α, inhibits AP-2 activity. Besides subscribing to the AP-2 complex, AP-2α, AP-2β and AP-2γ proteins compose the OB2-1 transcription factor complex. OB2-1 specifically upregulates expression of the proto-oncogene c-ErbB-2, which is overexpressed in 25-30% of breast cancers. AP-2α may play an important role in the development of ectodermal-derived tissues. Deleterious mutations involving the AP-2α gene are linked to microphthalmia, corneal clouding and other anterior eye chamber defects. The ubiquitously expressed AP-4 transcription factor specifically binds to the DNA consensus sequence 5'-CAGCTG-3'. AP-4 interacts with promoters for immunoglobulin-κ gene families and simian virus 40. AP-4 may enhance the transcription of the human Huntington's disease gene. AP-4 is a helix-loop-helix protein that contains two distinctive leucine repeat elements.