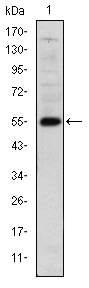
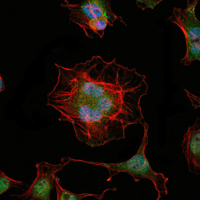
During development, genetically distinct subtypes of motor neurons express unique combinations of LIM-type homeodomain factors, which regulate cell migration and guide motor axons to establish the fidelity of a binary choice in axonal trajectory. The LIM gene family encodes a set of gene products, which carry the LIM domain, a unique cysteine-rich zinc-binding domain. The overlapping expression of LHX1, LHX3, LHX4, Isl-1 and Isl-2 in developing motor neurons along the spinal column may influence the establishment of specific motor neuron subtypes. The human LHX2 gene maps to chromosome 9q33.3 and encodes a 389 amino acid protein. LHX2 is involved in early patterning of the telencephalon, where the neuroepithelium is first divided into cortical tissue and cortical hem.