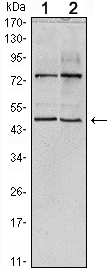
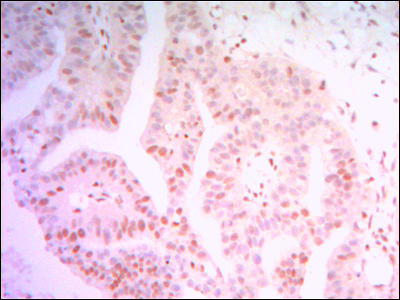
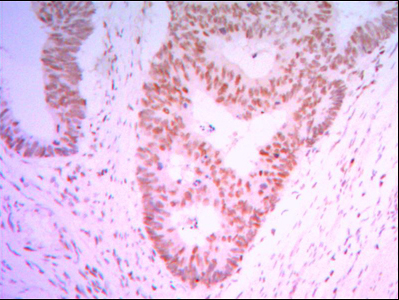
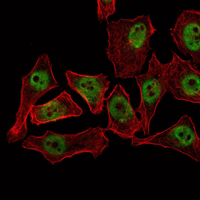
Members of the THAP (thanatos-associated protein) family of proteins contain a well conserved DNA-binding domain known as the THAP-type zinc finger motif. Proteins containing the THAP-type zinc finger motif are commonly involved in transcriptional regulation, cell-cycle control, apoptosis and chromatin modification. The THAP-type zinc finger domain is suggested to have similarities with the site-specific DNA-binding domain (DBD) of Drosophila P element transposase. THAP11 (THAP domain containing 11), also known as HRIHFB2206, is a 314 amino acid protein that belongs to the THAP11 family and contains one THAP-type zinc finger. Localizing to the nucleus and cytoplasm, THAP11 may act as a transcriptional repressor, playing a role in embryogenesis and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells by recruiting epigenetic modifiers. THAP11 interacts with HCF1 via a coiled coil domain.