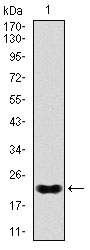
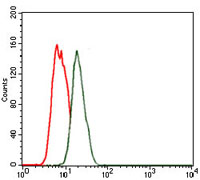
Members of the NK-2 family of homeodomain proteins are key regulators of growth and development in several tissues, including brain, heart and pancreas. During neural development, sonic hedgehog (Shh) is known to control cell fate and mitogenesis, which is correlated with Shh dose-dependent expression of several genes, including Nkx-2.1, Nkx-2.2 and Nkx-2.9. Specifically, the Nkx-2.2 protein is responsible for directing ventral neuronal patterning in response to graded Shh signaling. In the pancreas, Nkx-2.2 is expressed in a, b and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells, but not in d cells. Nkx-2.2 expression is required for differentiation of pancreatic b cells, which produce insulin. Homozygous null mutations of the Nkx-2.2 gene in mice lead to severe hyperglycemia and death shortly after birth, which suggests that Nkx-2.2 may be an important therapeutic target for pancreatic diseases, including diabetes and cancer.