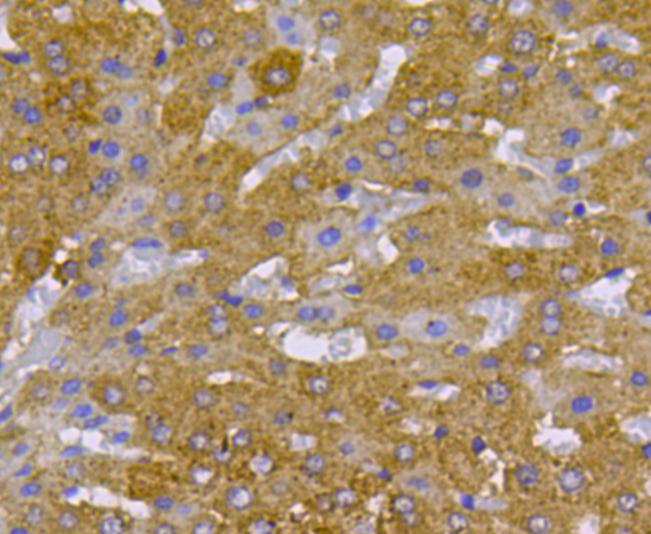
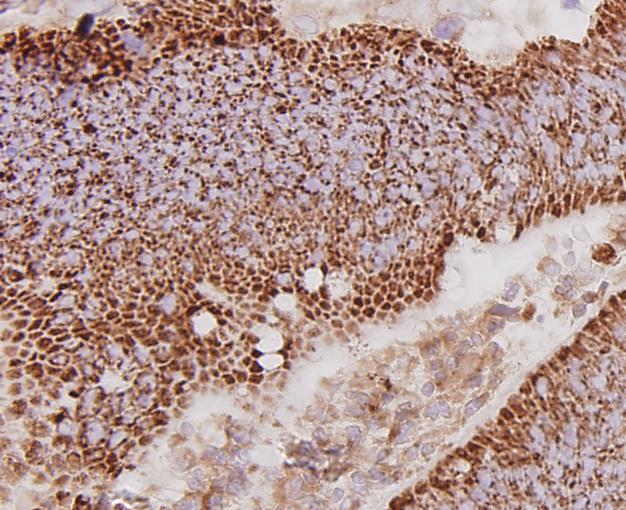
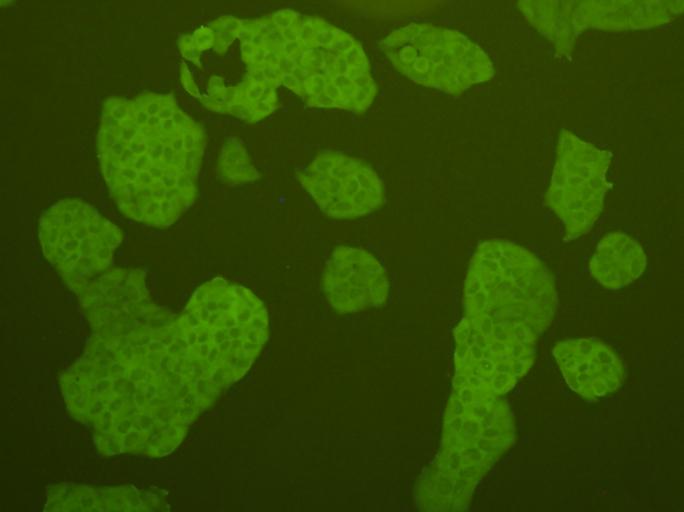
c-Met (MET or MNNG HOS Transforming gene) is a proto-oncogene that encodes a protein known as hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR). MET is a membrane receptor that is essential for embryonic development and wound healing. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is the only known ligand of the MET receptor. MET is normally expressed by cells of epithelial origin, while expression of HGF is restricted to cells of mesenchymal origin. Upon HGF stimulation, MET induces several biological responses that collectively give rise to a program known as invasive growth. Abnormal MET activation in cancer correlates with poor prognosis, where aberrantly active MET triggers tumor growth, formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) that supply the tumor with nutrients, and cancer spread to other organs (metastasis). MET is deregulated in many types of human malignancies, including cancers of kidney, liver, stomach, breast, and brain.