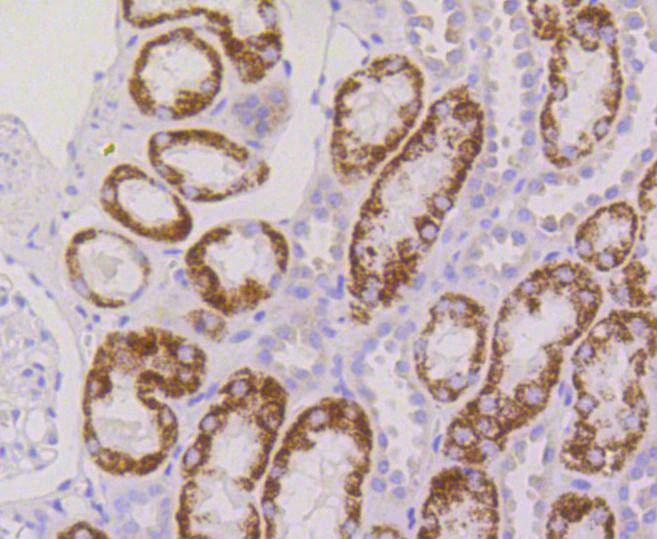
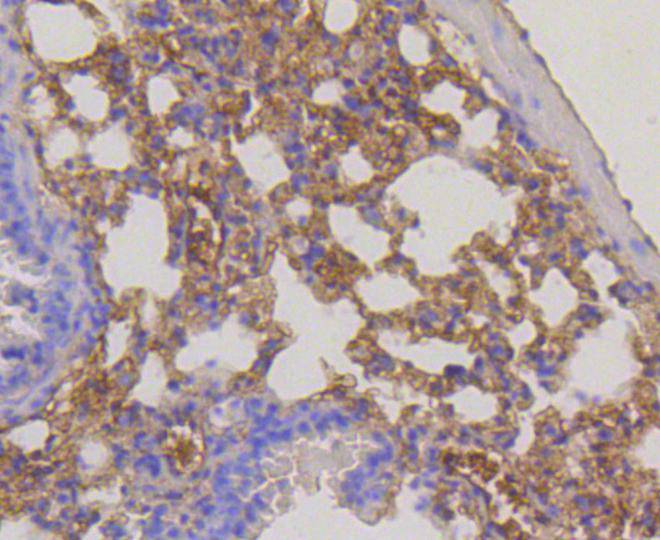
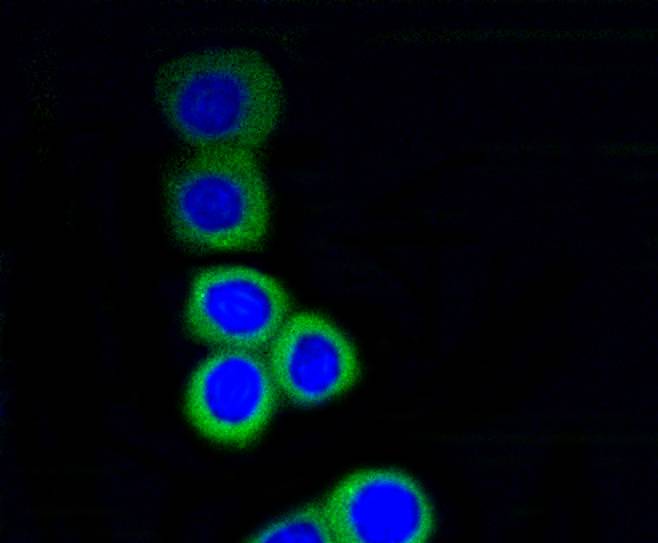
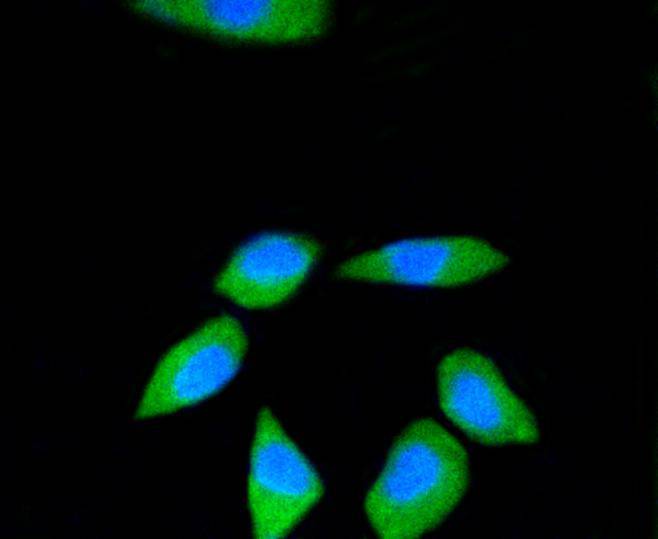
Ribosomal subunits are synthesized in the nucleus, and mature 40S and 60S subunits are exported stoichiometrically into the cytoplasm. Both 40S and 60S subunits are composed of four RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. Mitochondrial ribosomes consist of a small 28S subunit and a large 39S subunit. Ribosomal proteins have the ability to pass through the nuclear envelope in the native state, making them the largest of the structures accommodated by the nuclear pore complexes. The nuclear export of ribosomal subunits is a unidirectional, saturable and energy-dependent process. Ribosomal Protein S3 a member of the 40S subunit and plays a role in translation and ribosome maturation. Specifically, Ribosomal Protein S3 mediates the formation of the mRNA binding site 3 of the codon in the decoding site. In addition, Ribosomal Protein S3 is involved in DNA damage recognition as shown by its affinity for abasic sites and 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine residues and its interaction with human base excision repair (BER) proteins OGG1 and Ref-1.