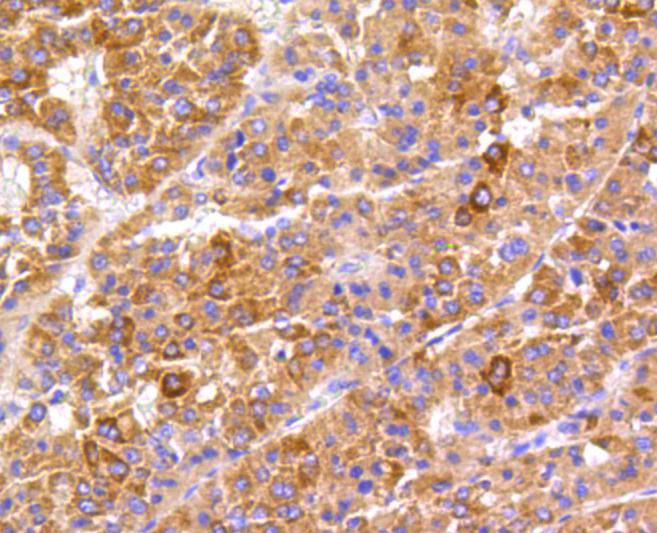
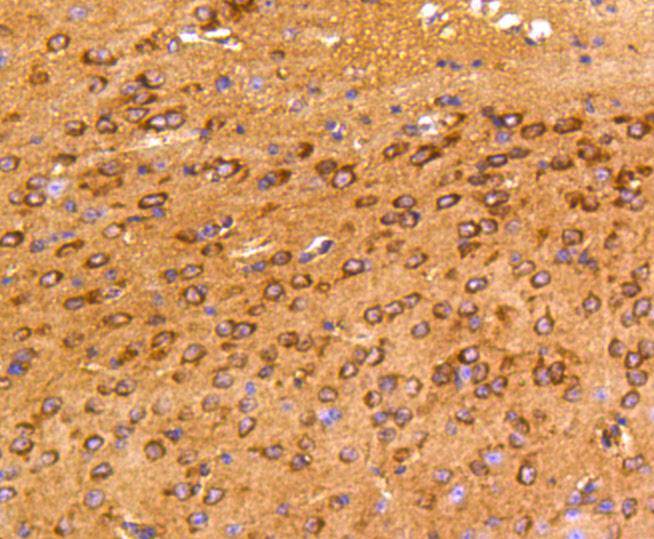
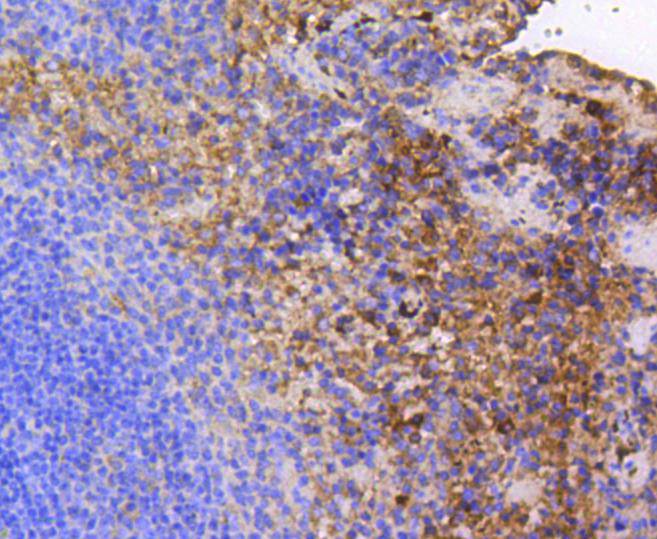
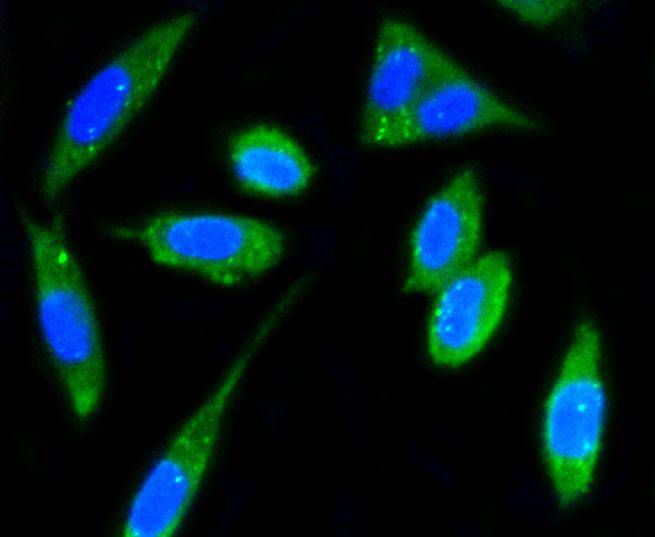
Focal adhesion kinase was initially identified as a major substrate for the intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase activity of Src encoded pp60. The deduced amino acid sequence of FAK p125 has shown it to be a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase whose sequence and structural organization are unique as compared to other proteins described to date. Localization of p125 by immunofluorescence suggests that it is primarily found in cellular focal adhesions leading to its designation as focal adhesion kinase (FAK). FAK is concentrated at the basal edge of only those basal keratinocytes that are actively migrating and rapidly proliferating in repairing burn wounds and is activated and localized to the focal adhesions of spreading keratinocytes in culture. Thus, it has been postulated that FAK may have an important in vivo role in the reepithelialization of human wounds. FAK protein tyrosine kinase activity has also been shown to increase in cells stimulated to grow by use of mitogenic neuropeptides or neurotransmitters acting through G protein coupled receptors.