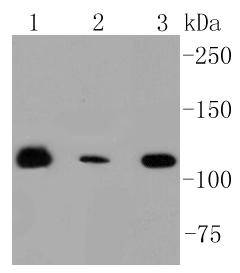
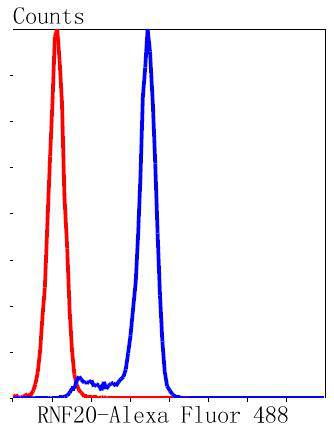
Ubiquitination is an important mechanism through which three classes of enzymes act in concert to target short-lived or abnormal proteins for destruction. The three classes of enzymes involved in ubiquitination are the ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) and the ubiquitin-protein ligases (E3s). RNF20 (ring finger protein 20), also known as BRE1, BRE1A or hBRE1, is a 975 amino acid nuclear protein that belongs to the BRE1 family. As a component of the RNF20/40 complex, RNF20 functions as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that regulates the monoubiquitination and subsequent degradation of select residues on target proteins, such as Histone H2B. RNF20 is required for transcriptional activation of Hox genes and is most likely recruited by p53 to the MDM2 promoter, thereby acting as a transcriptional co-activator. RNF20 contains one zinc finger domain and exists as a homodimer.