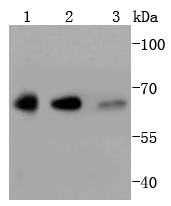
The YY1 transcription factor, also known as NF-E1 (human) and Delta or UCRBP (mouse) is of interest due to its diverse effects on a wide variety of target genes. YY1 is broadly expressed in a wide range of cell types and contains four C-terminal zinc finger motifs of the Cys-Cys-His-His type and an unusual set of structural motifs at its N-terminal. It binds to downstream elements in several vertebrate ribosomal protein genes, where it apparently acts positively to stimulate transcription and can act either negatively or positively in the context of the immunoglobulin k 3' enhancer and immunoglobulin heavy-chain μE1 site as well as the P5 promoter of the adeno-associated virus. It thus appears that YY1 is a bifunctional protein, capable of functioning as an activator in some transcriptional control elements and a repressor in others.