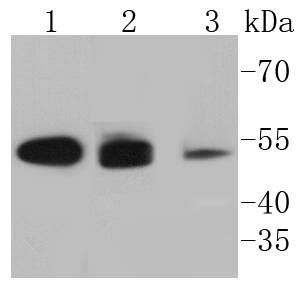
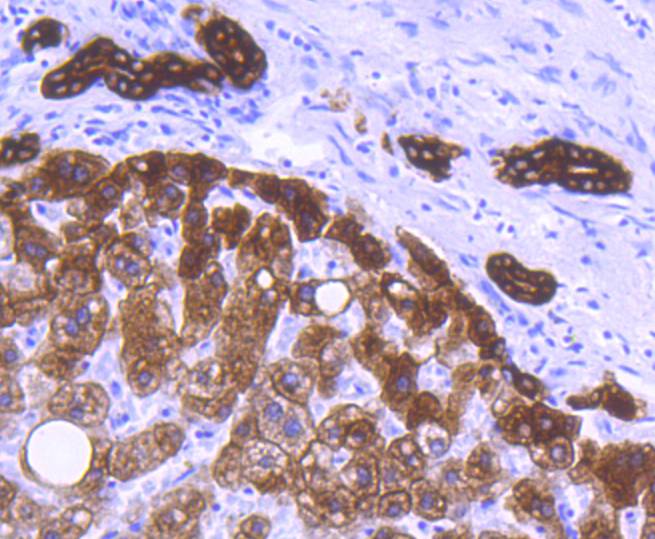
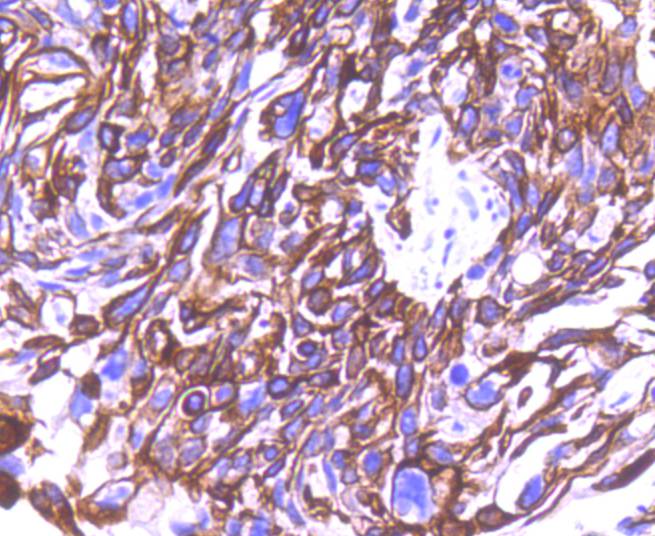
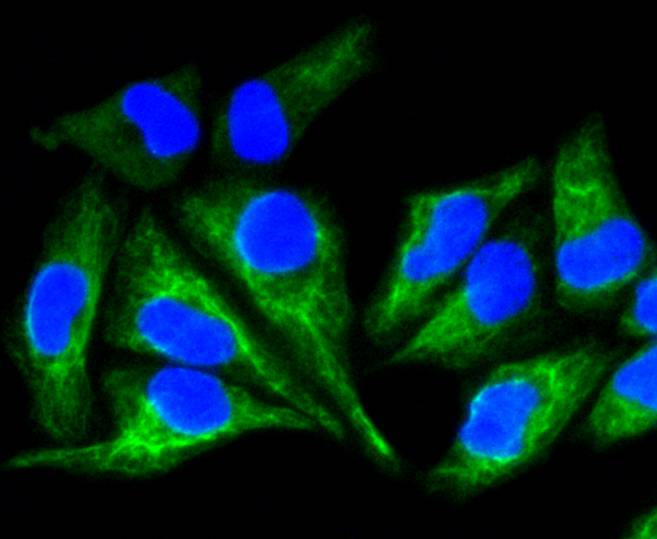
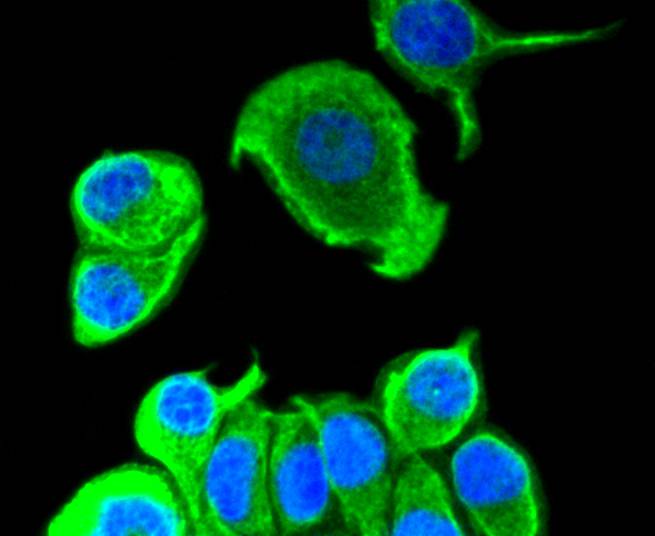
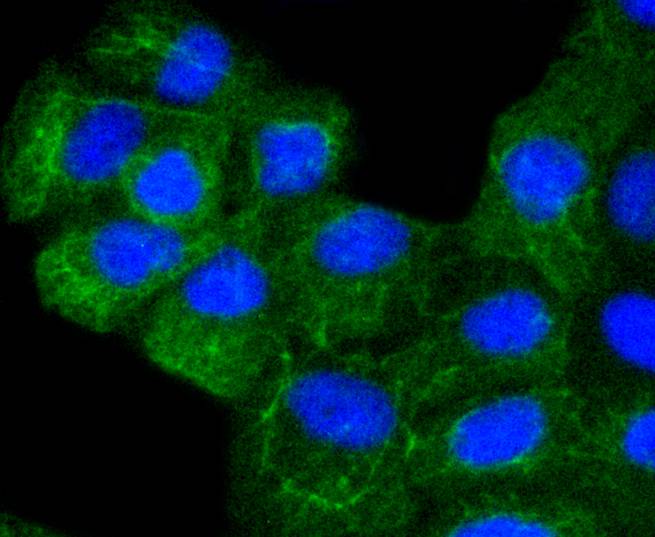
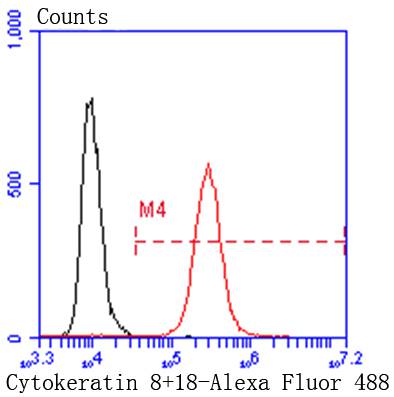
Cytokeratins comprise a diverse group of intermediate filament proteins (IFPs) that are expressed as pairs in both keratinized and non-keratinized epithelial tissue. Cytokeratins play a critical role in differentiation and tissue specialization and function to maintain the overall structural integrity of epithelial cells. They have been found to be useful markers of tissue differentiation, which is directly applicable to the characterization of malignant tumors. Cytokeratin 8 expression is seen in epithelium and epithelium-derived tumors. The Cytokeratin 8 and 18 pair are normally expressed in simple epithelia, but not in stratified epithelial cells. Research indicates that squamous cell carcinomas derived from stratified epithelia show abnormal expression of Cytokeratin 8 and 18, although it is not known whether these proteins contribute to the malignant phenotype of the cells. Expression of Cytokeratin 8 and 18 in oral squamous cell carcinomas is an independent prognostic marker that indicates a poor prognosis. Cytokeratin 8 expression correlates with malignancy in leukoplakia and carcinomas of the head and neck; it is expressed in all non-small-cell lung cancers. Cytokeratin 8 has been shown to possess extracellular epitopes on tumor cells, which may represent valuable targets for therapy.