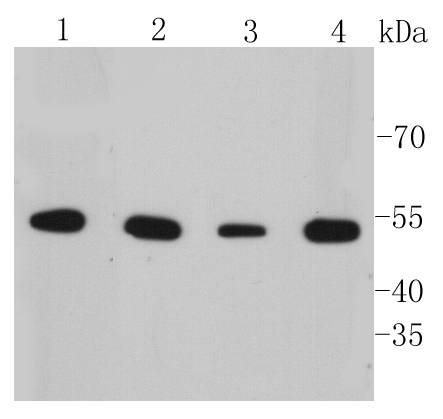
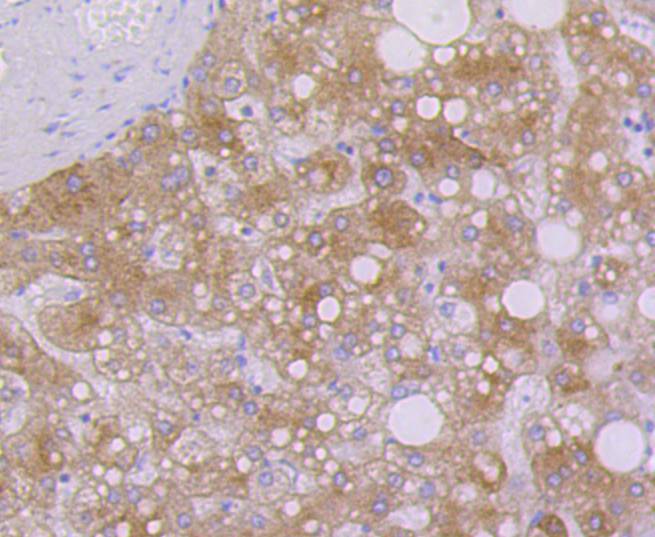
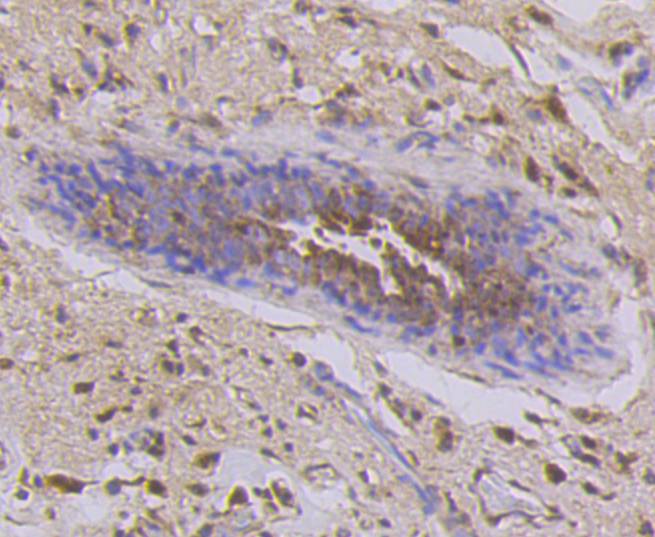
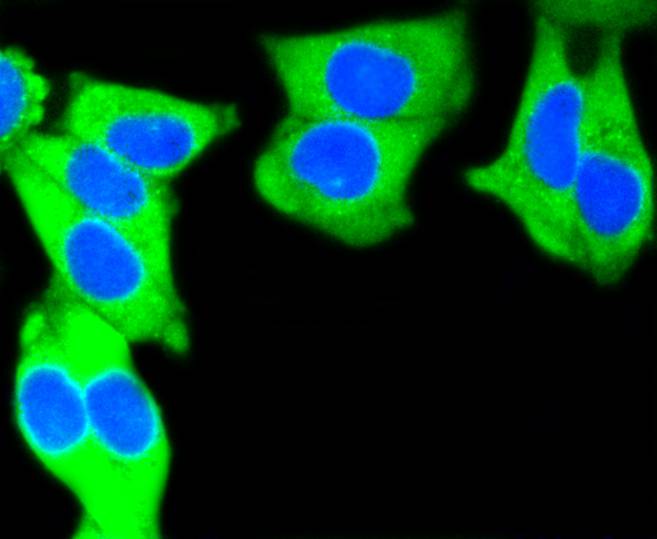
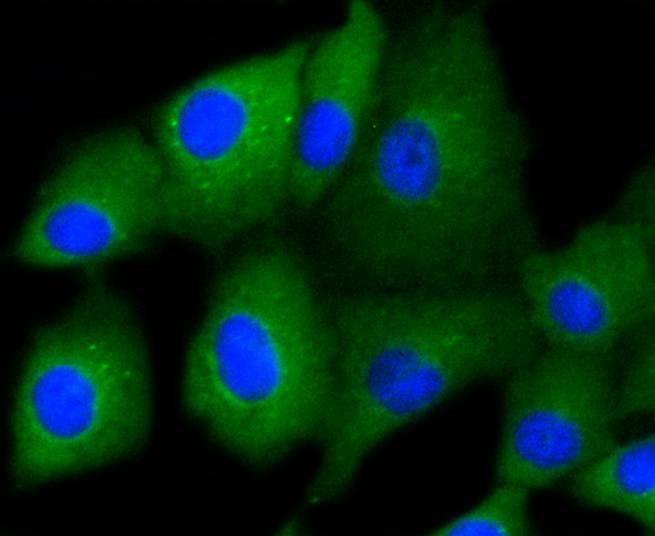
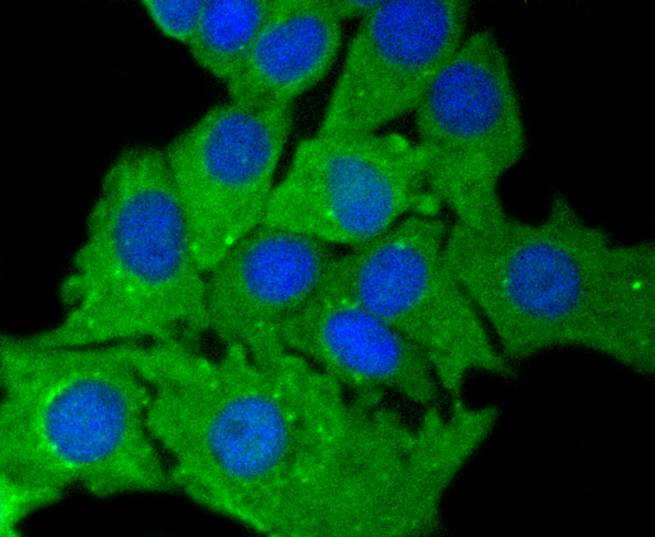
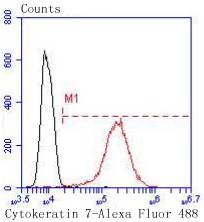
Cytokeratins comprise a diverse group of intermediate filament proteins (IFPs) that are expressed as pairs in both keratinized and non-keratinized epithelial tissue, where they constitute up to 85% of mature keratinocytes in the vertebrate epidermis. Cytokeratins play a critical role in differentiation and tissue specialization and function to maintain the overall structural integrity of epithelial cells. The a-helical coiled-coil dimers associate laterally end-to-end to form 10 nm diameter filaments. Cytokeratins are useful markers of tissue differentiation and, in addition, they aid in the characterization of malignant tumors. Cytokeratin 7 (also known as sarcolectin) agglutinates normal and transformed cells with a high affinity for simple sugars. Cytokeratin 7 also inhibits the synthesis of interferon-dependent secondary proteins thus reversing the antiviral effect of interferon induction and restoring cells to their status ad primum. In normal and transformed cells, Cytokeratin 7 localizes to the membrane.