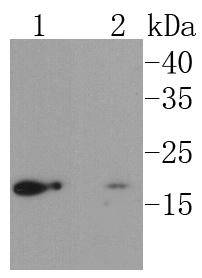
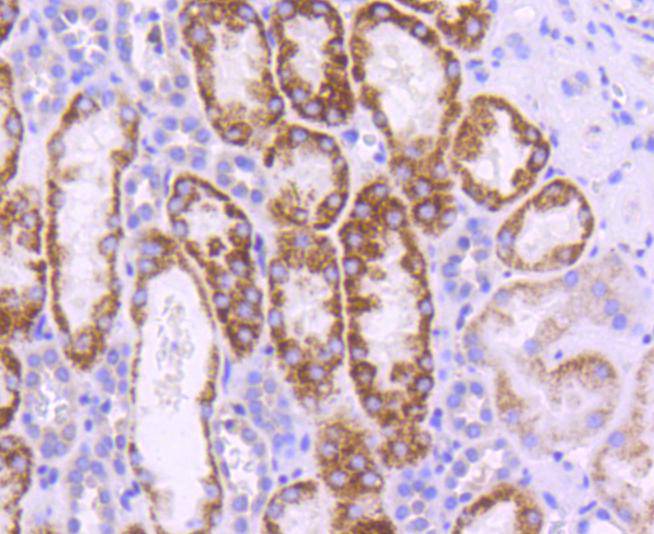
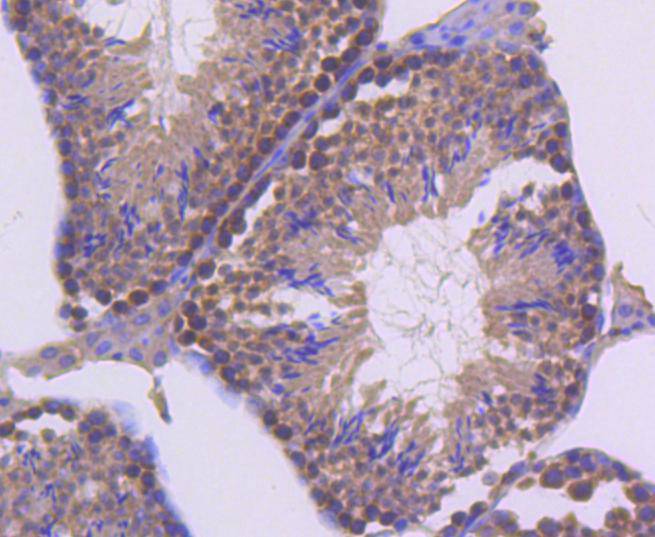
UBC9 is a component of the ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway, which targets proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome, mediates endocytosis and directs protein subcellular localization. Ub and Ub-like molecules are systematically transferred from E2 conjugating enzymes to the targeted substrate by way of an E3 ubiquitin ligase. UBC9 functions as an E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme that preferentially associates with the ubiquitin homolog designated SUMO-1 or sentrin, a component of the sentrinization complex. Characteristic of the E2 family members, UBC9 contains a conserved cysteine residue that is required for the thio ester formation between Ub-like proteins and the E2 member, and it shares a conserved UBC domain. Substrates for UBC9 include transcription factors E12 and E47 and mitotic regulators RanBP2 and RanGAP1, which indicates that UBC9 may regulate various cellular processes including cell cycle progression and differentiation.