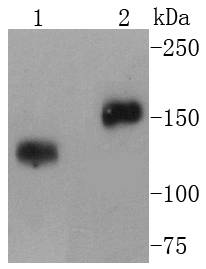
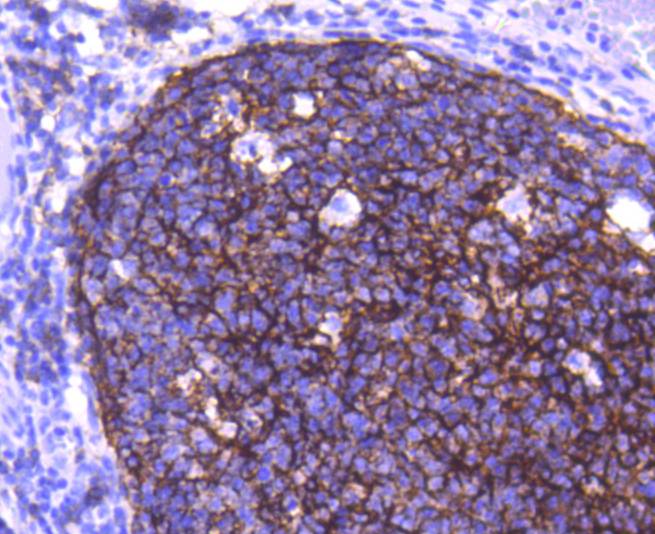
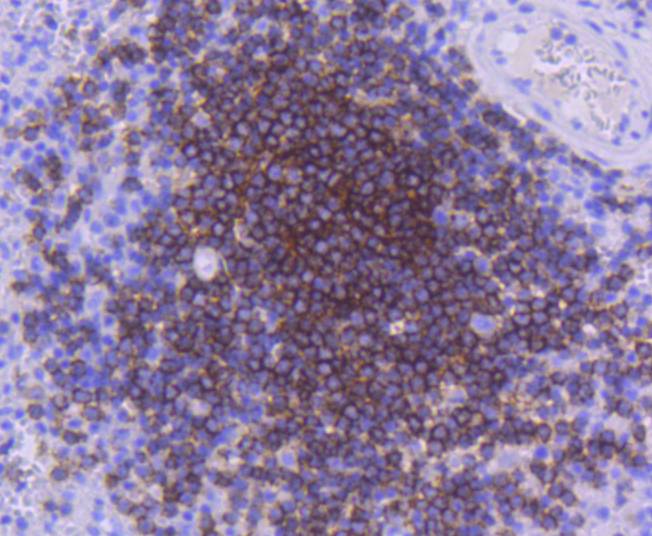
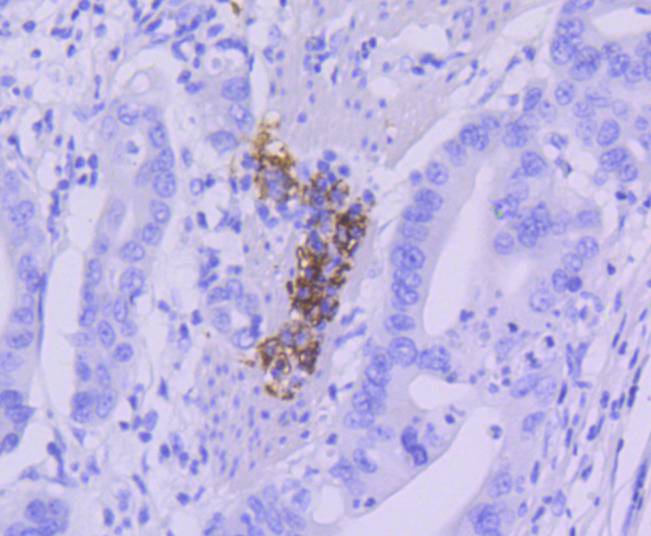
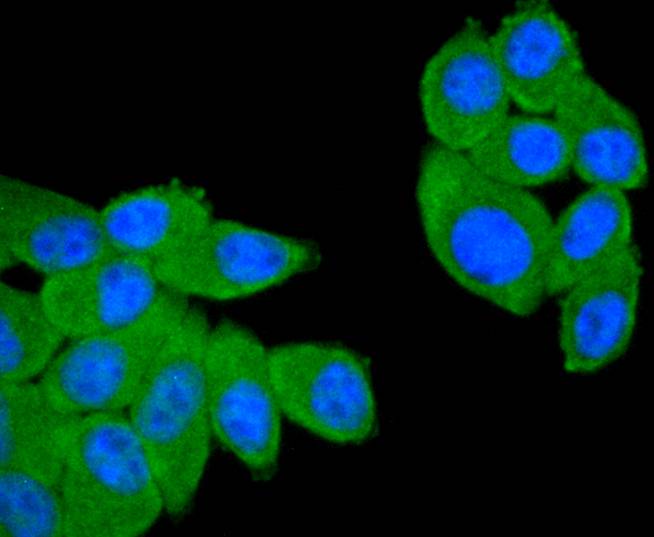
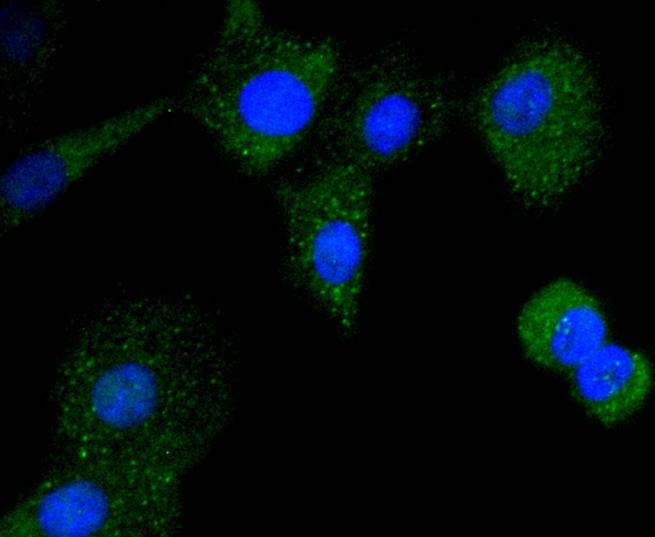
CD21 is a type I integral membrane glycoprotein that serves as a receptor for the C3d complement fragment and for the Epstein-Barr virus. It plays a role in B cell activation and proliferation and undergoes phosphorylation after B cell activation with phorbol esters. CD21 is expressed on mature B cells, follicular dendritic cells, pharyngeal and cervical epithelial cells and a subset of thymocytes. The adaptive immune response is tightly regulated to limit responding cells in an antigen-specific manner. On B cells, co-receptors CD21/CD19 modulate the strength of B cell Ag receptor (BCR) signals, thereby influencing cell fate. Complement receptor (CR) type 2 (CR2/ CD21) is normally expressed during the immature and mature stages of B cell development. In association with CD19, CR21 plays an important role in enhancing mature B cell responses to foreign antigens.