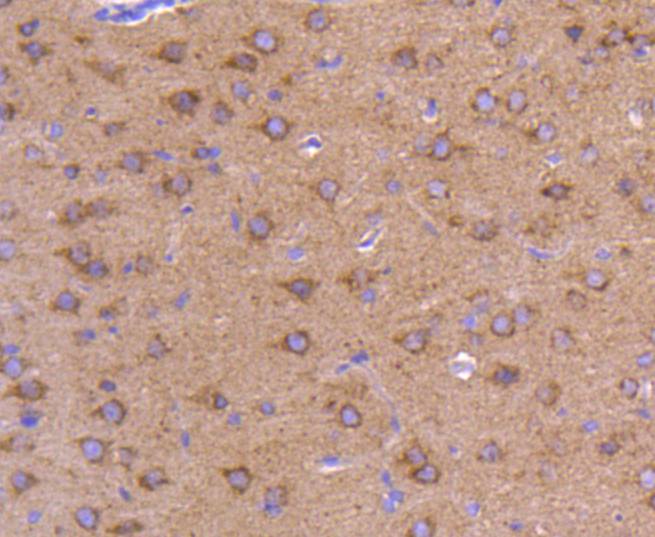
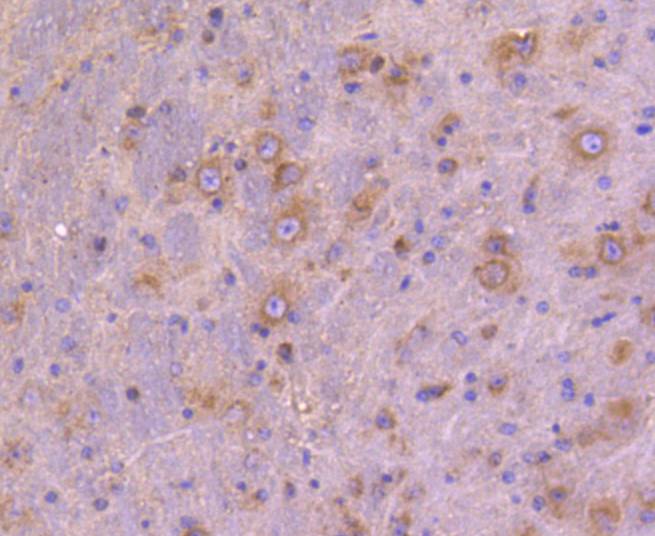
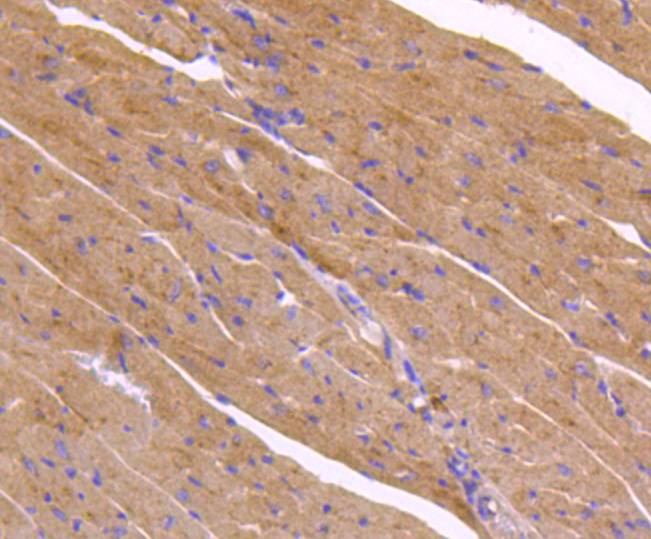
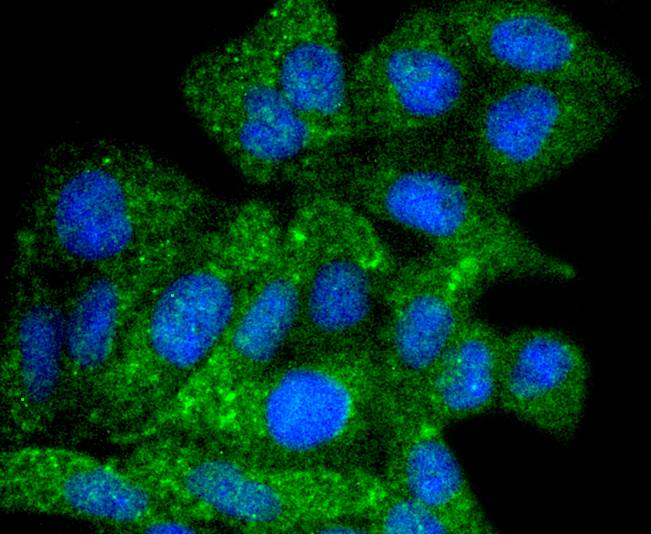
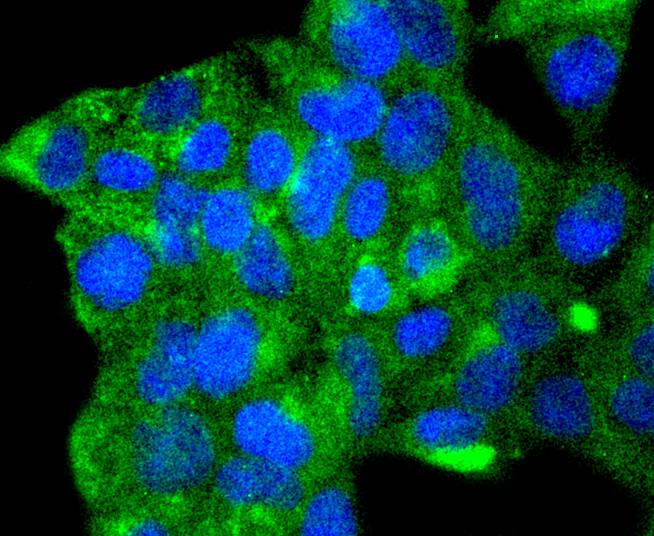
Autophagy, a process that results in the lysosomal-dependent degradation of cytosolic compartments, is carried out by the autophagosome, which is a double-membrane vesicle whose formation is catalyzed by several autophagy-related gene (Atg) proteins. Atg9a (autophagy-related protein 9A), also known as APG9-like 1, is a 839 amino acid, multi-pass membrane protein that localizes to the pre-autophagosomal structure (PAS). Isolation membranes are suggested to originate from the PAS, enwrapping cytoplasmic components to form a double membrane autophagosome, which then fuses with the vacuole. Ubiquitously expressed in human adult tissues, Atg9a cycles between the Golgi and endosomes and, with the autophagosome-specific marker LC3, plays a critical role in starvation-induced autophagosome formation. Three isoforms of Atg9a exist as a result of alternative splicing events.