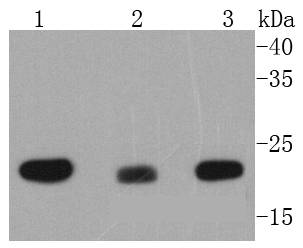
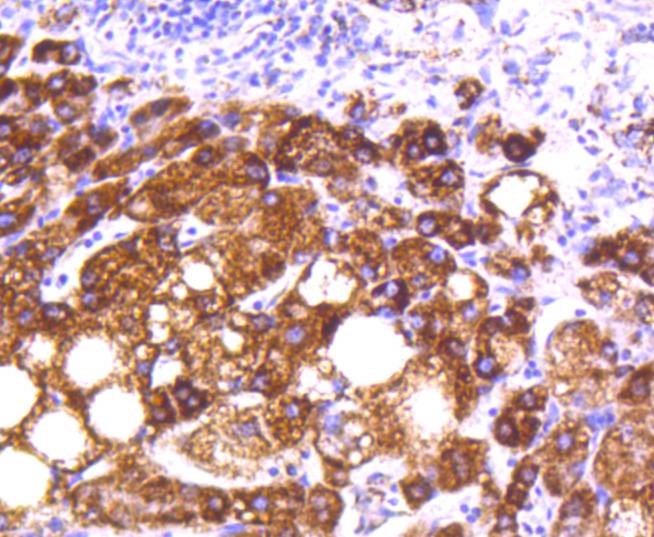
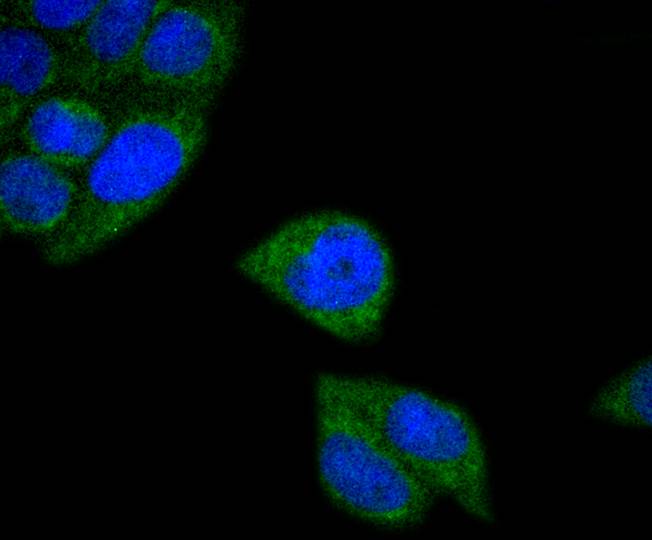
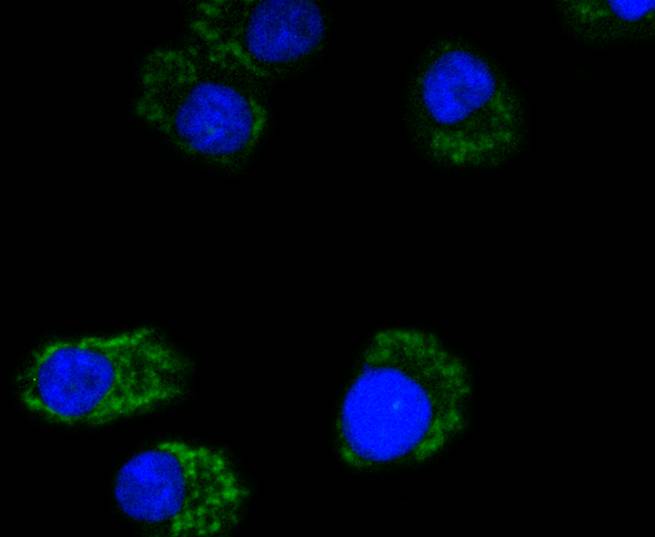
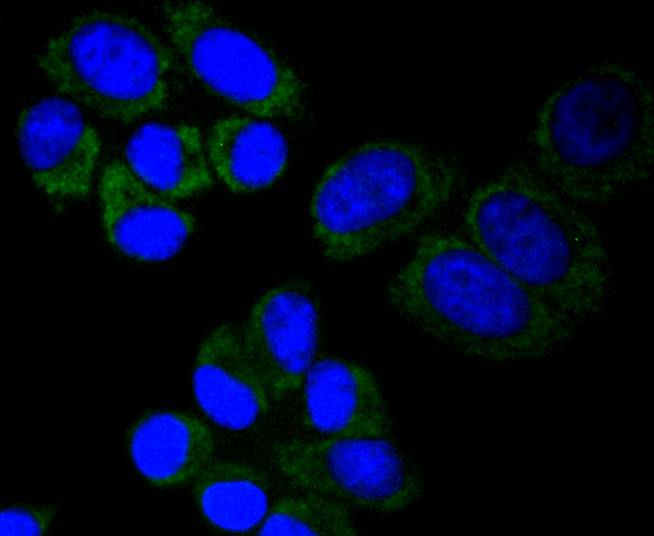
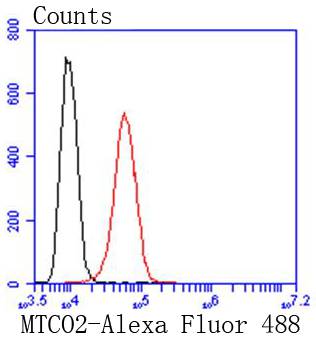
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II (COX2), also designated COII, MTCO2 or oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) complex IV, subunit II, is one of three mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encoded subunits (MTCO1-3) of respiratory complex IV. Cytochrome c oxidase is a hetero-oligomeric enzyme composed of 13 subunits localized to the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the terminal enzyme complex of the electron transport chain. Complex IV catalyzes the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. The energy released is used to transport protons across the mitochondrial inner membrane. The resulting electrochemical gradient is necessary for the synthesis of ATP. Complex IV contains 13 polypeptides; COX1, COX2 and COX3 (MTCO1-3) make up the catalytic core and are encoded by mtDNA while subunits IV, Va, Vb, VIa, VIb, VIc, VIIa, VIIb, VIIc and VIII are nuclear-encoded. Defects in COX2 are associated with tumor formation.