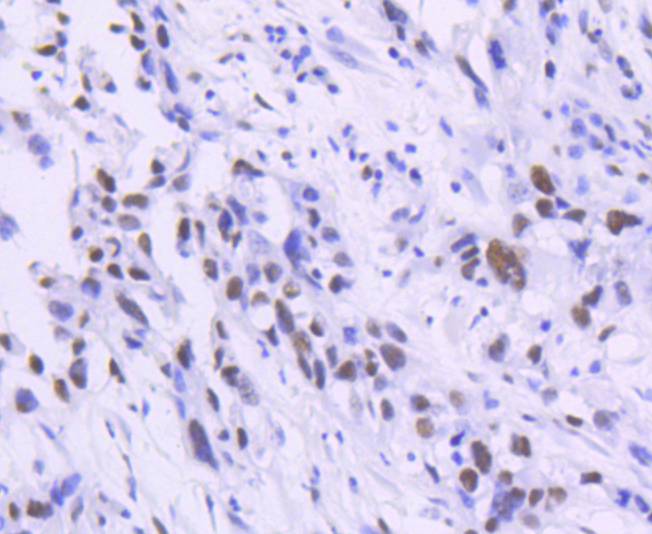
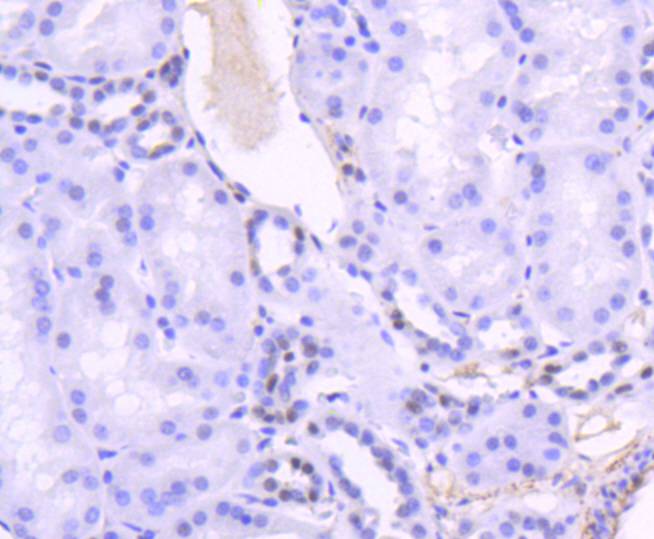
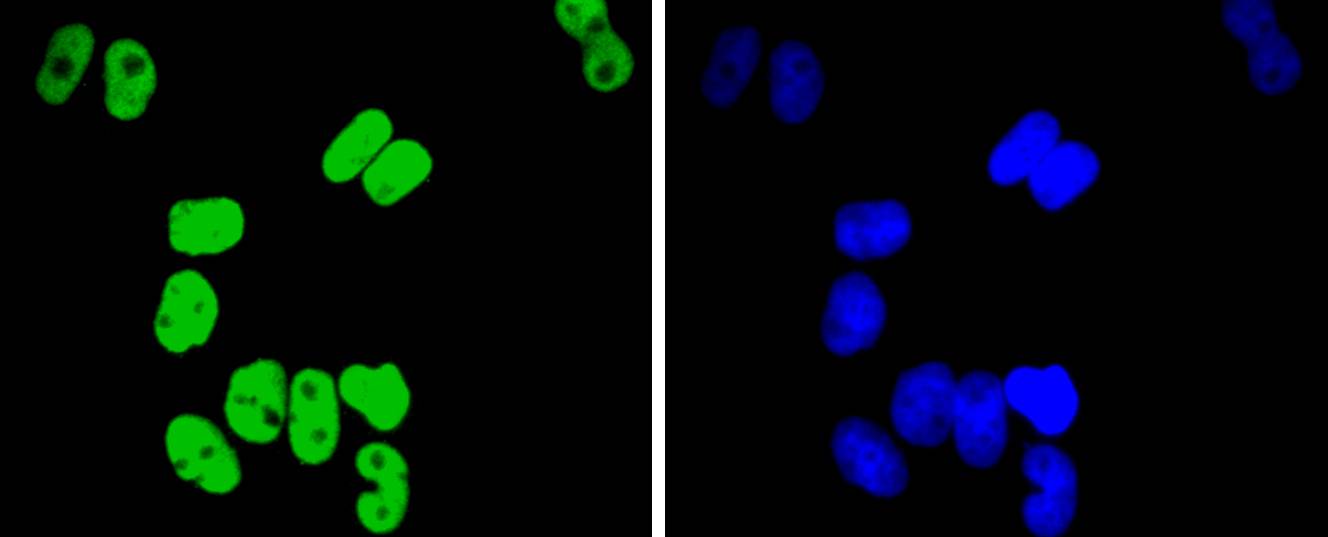
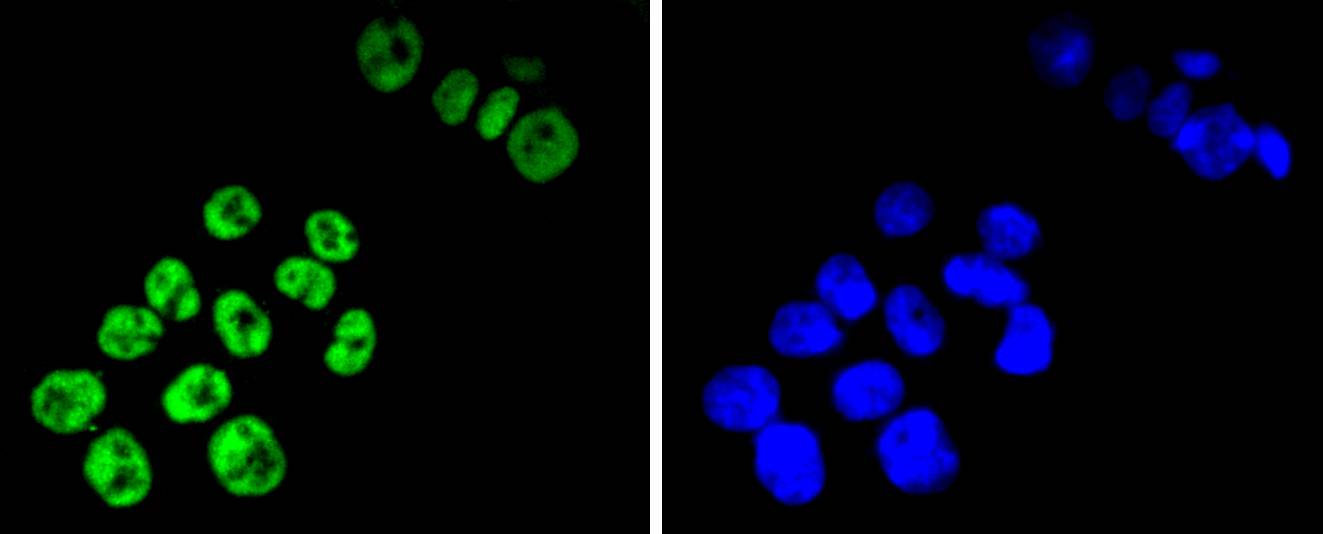
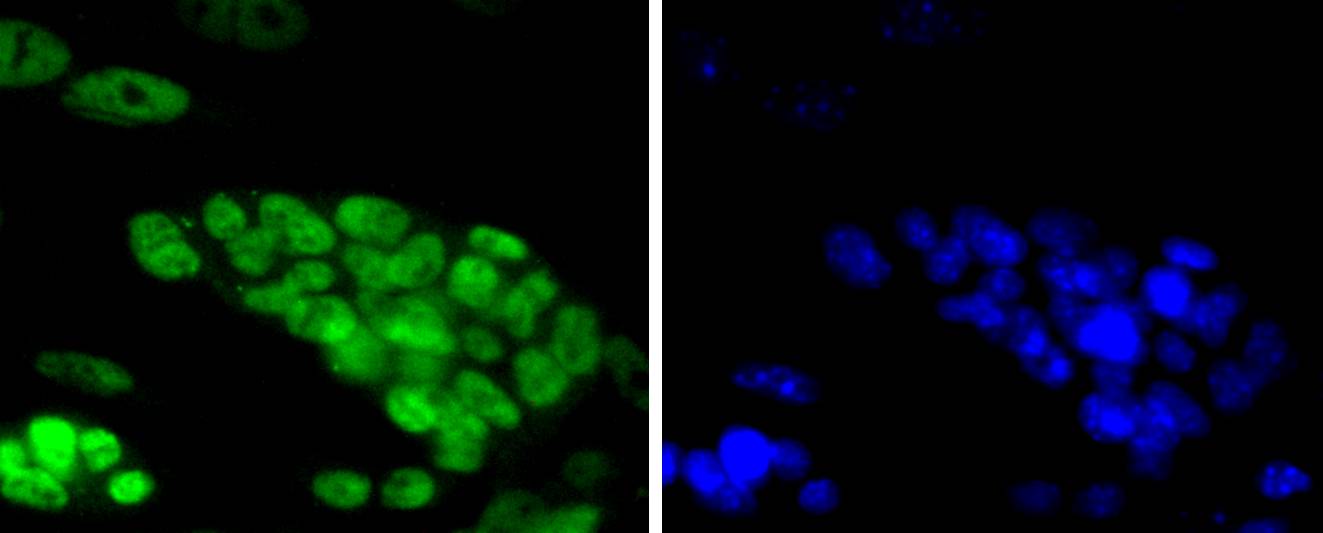
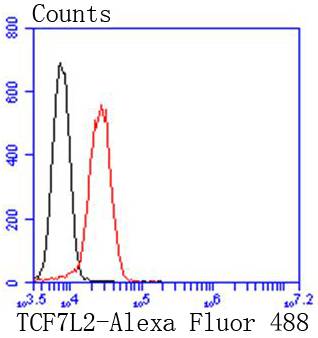
T cell factors (TCFs) comprise a family of DNA-binding transcriptional activators that are essential for lymphoid cell development. These transcription factors are activated by the Wnt-1 and Wingless pathways and are characterized by the presence of a conserved protein motif, the high mobility group (HMG) 1 box, which mediates DNA binding. TCF-4 mainly localizes in the cytoplasm and is transported into the nucleus directly bound to β-catenin in a cooperative manner. This TCF-4/β-catenin complex induces expression of Wnt target genes, including multiple cancer-associated genes. c-Jun also interacts with TCF-4 and β-catenin, and the phosphorylation-dependent interaction between c-Jun and TCF4 regulates intestinal tumorigenesis by integrating JNK and APC/β-catenin. TCF-4 is also implicated in bipolar affective disorder.