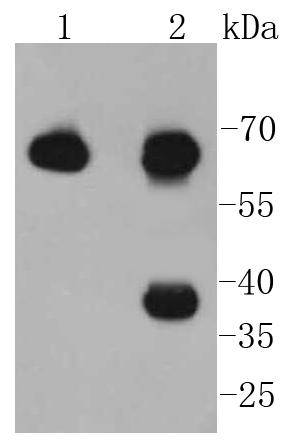
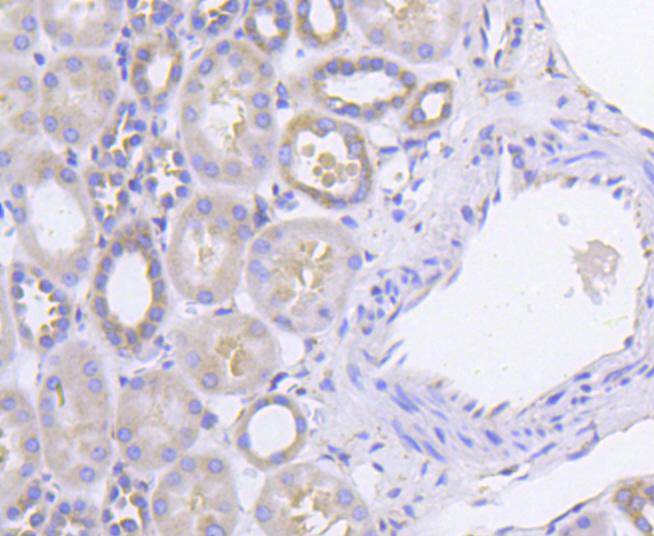
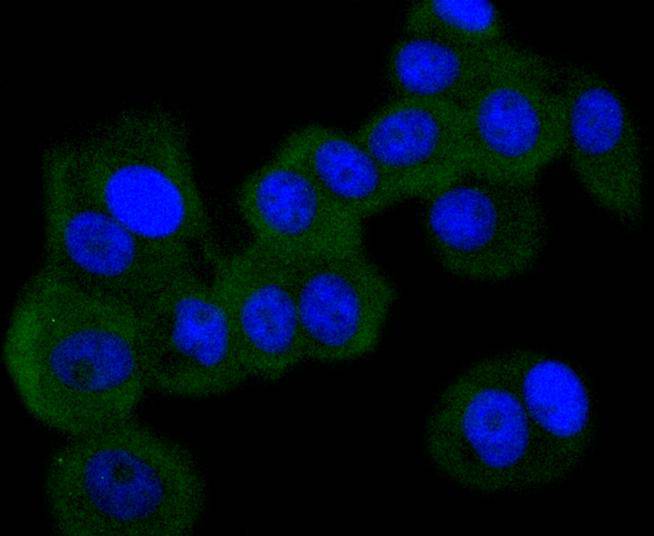
An interferon-inducible, RNA-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase (PKR) has been described. PKR in earlier literature is variously known as DAI, dsJ, PI kinase, p65, p67 or TIK for the mouse kinase; and p68 or p69 for the human kinase. The PKR kinase substrate is the a subunit of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2. Phosphorylation of eIF-2a on serine-51 results in inhibition of translation. Molecular cDNA clones have been isolated from both human and mouse cells. The serine/threonine kinase catalytic domains map to the carboxy terminal half of the protein while the RNA-binding domains are located in the amino terminal region. Three kinds of regulation of PKR enzymatic activity have been described. These include transcriptional regulation in response to interferon, an autoregulatory mechanism controlling PKR expression at the level of translation and post-translational regulation by RNA mediated autophosphorylation.