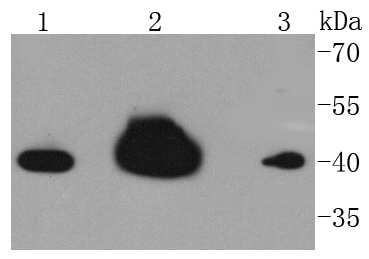
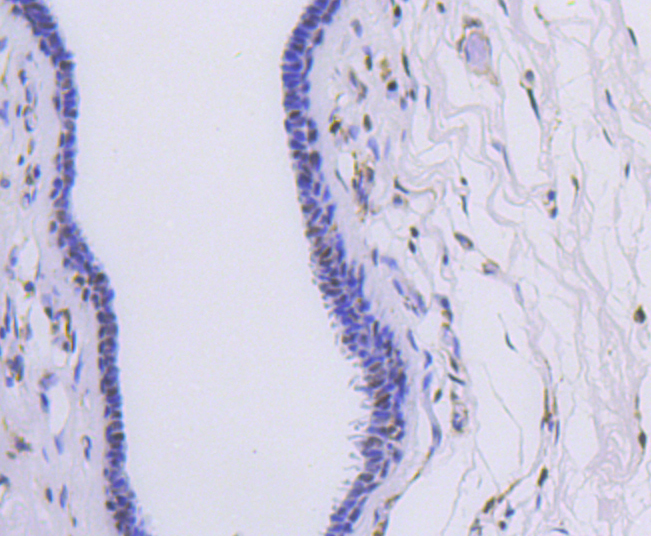
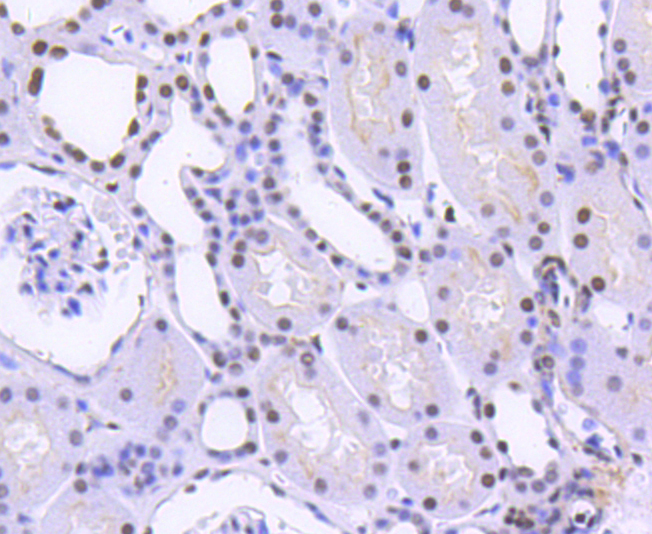
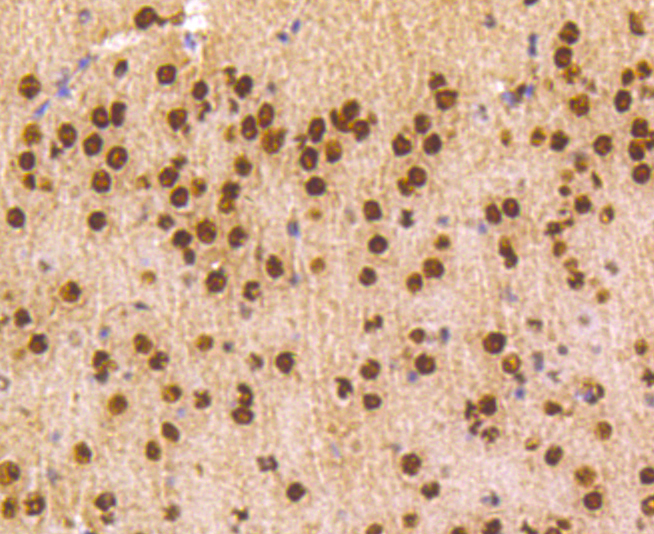
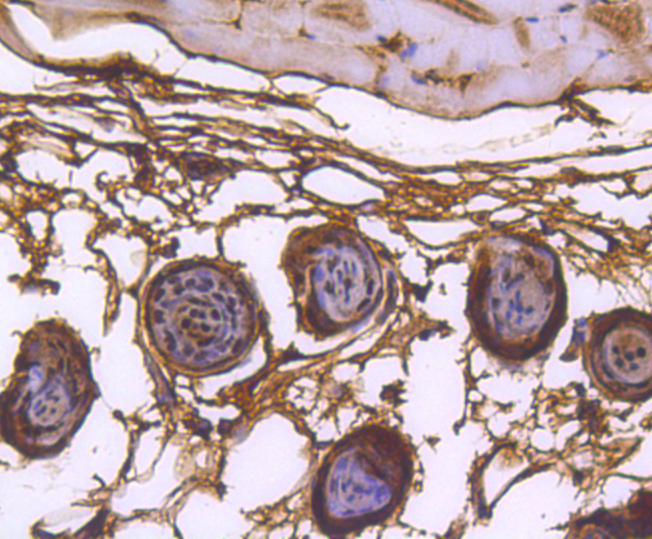
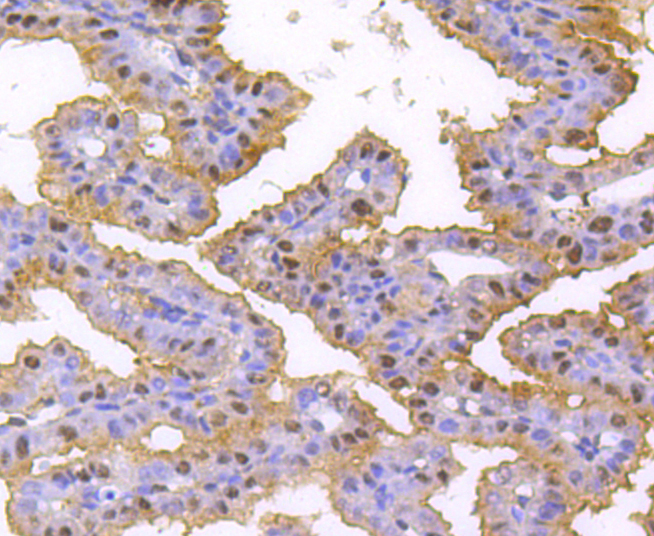
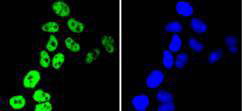
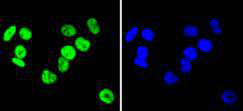
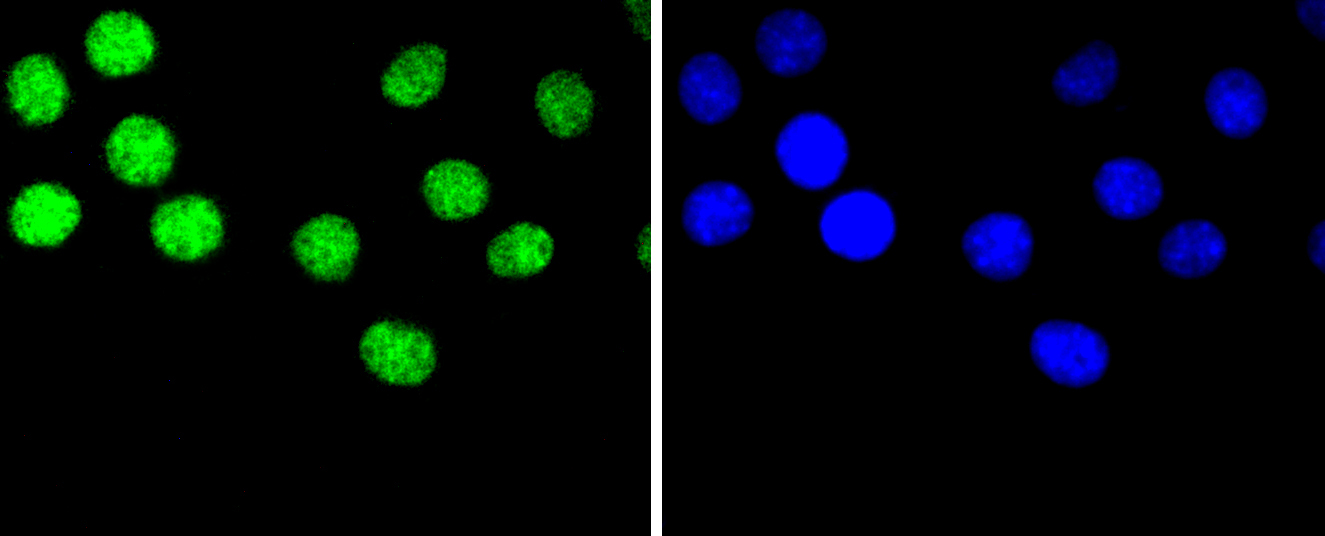
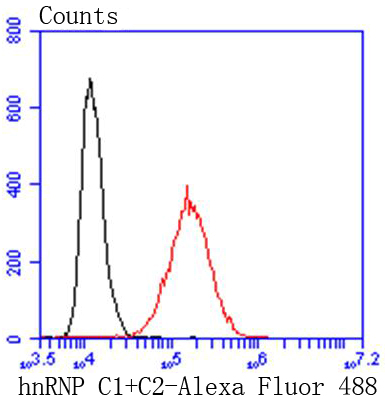
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) constitute a set of polypeptides that contribute to pre-mRNA processing and transport, and also bind heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA), which are the transcripts produced by RNA polymerase II. hnRNP complexes are the major constituents of the spliceosome and, in particular, the hnRNP A1 protein is one of the major pre-mRNA/mRNA binding proteins and also one of the most abundant proteins in the nucleus. hnRNP A1 and A2/B1 regulate the processing of pre-mRNA by directly antagonizing the association of various splicing factors and by influencing the splice site selection on pre-mRNA. The majority of hnRNP proteins components are localized to the nucleus; however, some shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Most hnRNP proteins, in-cluding hnRNP C1 and C2, contain one or more RNA binding domains and are implicated in the processing of pre-mRNA. hnRNPs F and H are largely related factors that preferentially associate with poly(rG) regions on RNA. Isoforms of these proteins are often generated by alternative processing of the pre-mRNA and by posttranslational modifications such as phosphorylation on serines and threonines and methylation of arginines.