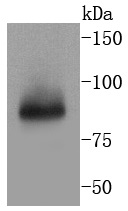
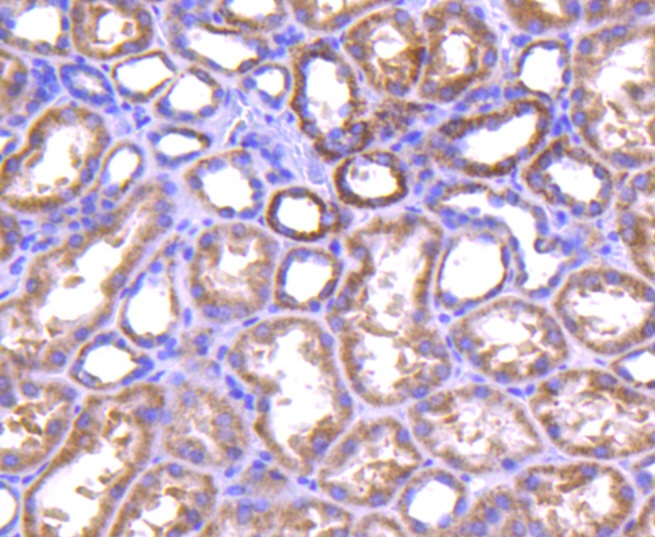
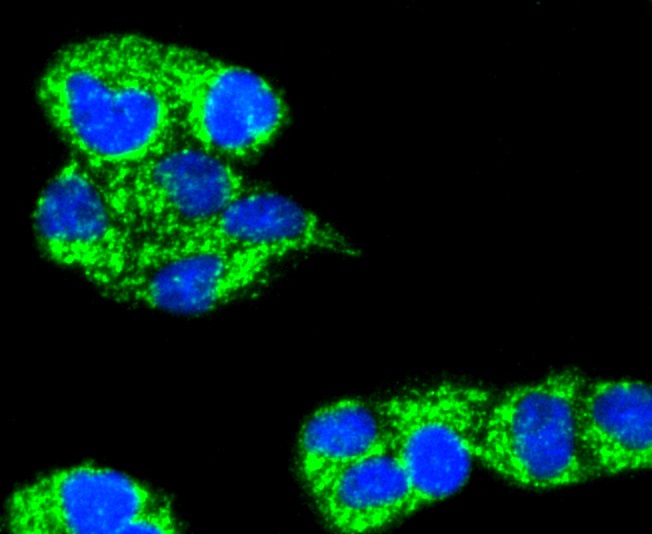
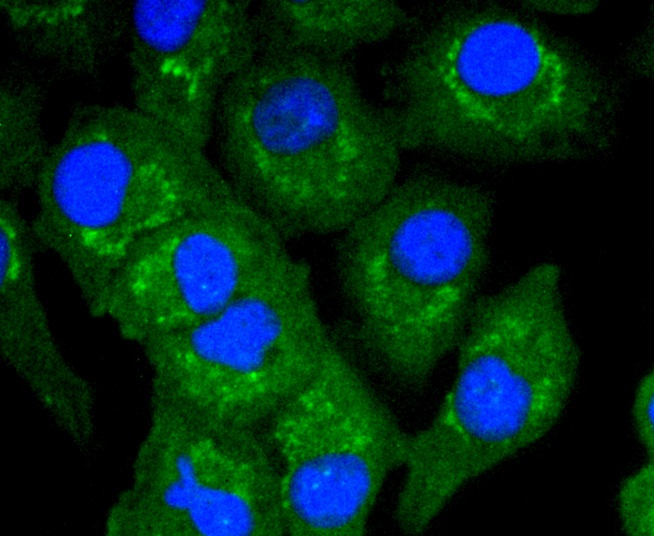
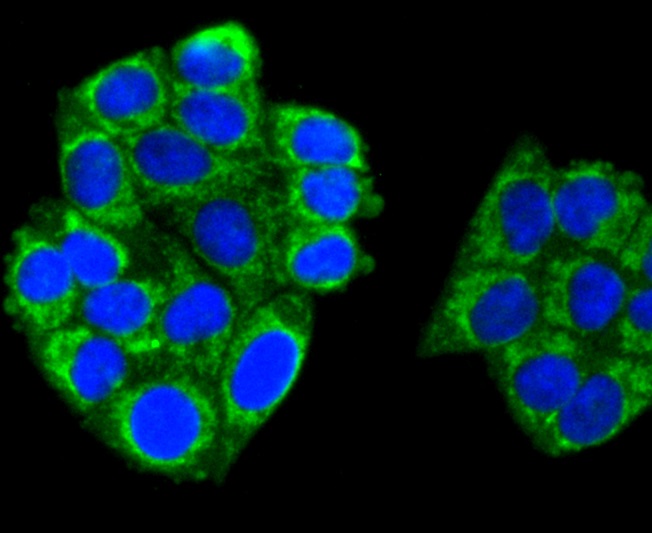
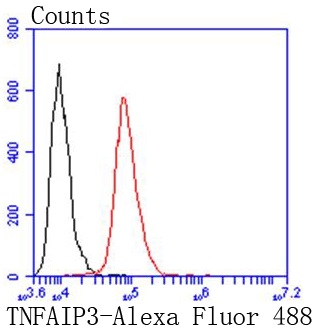
A20 is a Cys2/Cys2 zinc finger protein that is induced by a variety of inflammatory stimuli and regulates gene expression. Specifically, A20 is induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin 1 (IL-1), and acts as a negative regulator of nuclear factor κ B (NFκB) gene expression. By inhibiting NFκB activation, A20 plays a critical role in terminating NFκB responses to various stimuli. Although the C-terminal region of A20 contains seven zinc finger domains, only four of these domains are required for in vitro inhibition of TNF-induced NFκB activation. A20 also interacts with several other proteins, such as TRAF2, TRAF6 and IκB kinase (IKK) γ protein, and can thereby inhibit cell death. TXBP151, a novel A20-binding protein, may mediate the anti-apoptotic activity of A20. Involved in the negative feedback regulation of signal transduction, A20 and A20-binding proteins may be useful as novel therapeutic tools in the treatment of a variety of diseases.