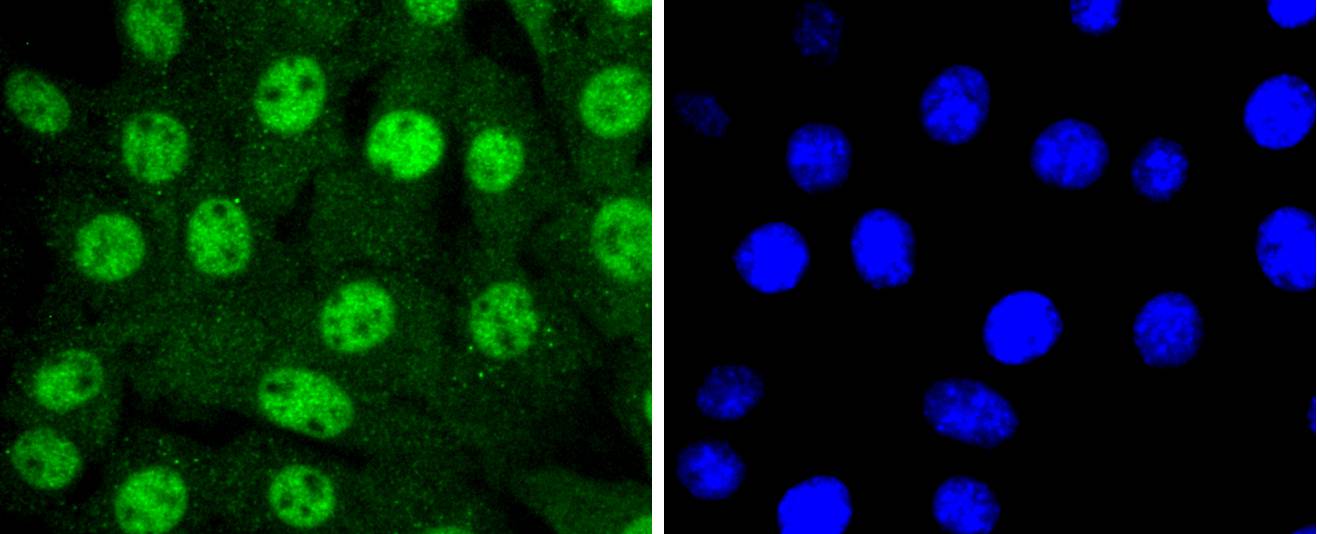
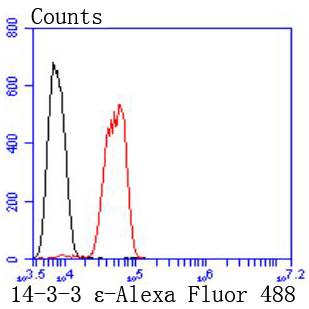
The 14-3-3 family of proteins plays a key regulatory role in signal transduction, checkpoint control, apoptotic and nutrient-sensing pathways. 14-3-3 proteins are highly conserved and ubiquitously expressed. There are at least seven isoforms, β, γ, ε, , ζ, and η that have been identified in mammals. The 14-3-3 epsilon, a subtype of the 14-3-3 family of proteins, was thought to be brain and neuron-specific. It has been shown to interact with CDC25 phosphatases, RAF1 and IRS1 proteins, suggesting its role in diverse biochemical activities related to signal transduction, such as cell division and regulation of insulin sensitivity. It has also been implicated in the pathogenesis of small cell lung cancer.