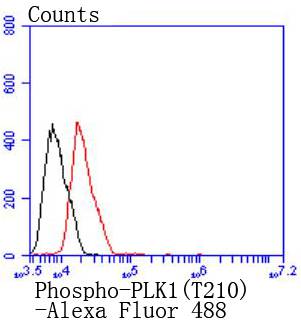
Plk (for polo-like kinase) encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is closely related to polo and CDC5, genes that are required for passage through mitosis in Drosophila and Saccharomyces, respectively. Polo and CDC5 both code for proteins that are involved in regulating the function of the mitotic spindle. Plk protein accumulates in the cell during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and both protein content and catalytic activity peak at the onset of mitosis, followed by a rapid reduction after mitosis. Plk expression is detectable in mitotically active tissues such as colon and placenta, as well as in tumors of various origins. It has also been suggested that Plk may serve as a marker of cell proliferation. The phosphorylation of mouse, rat and human Plk on Thr 210 enhances Plk catalytic activity.