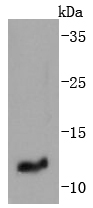
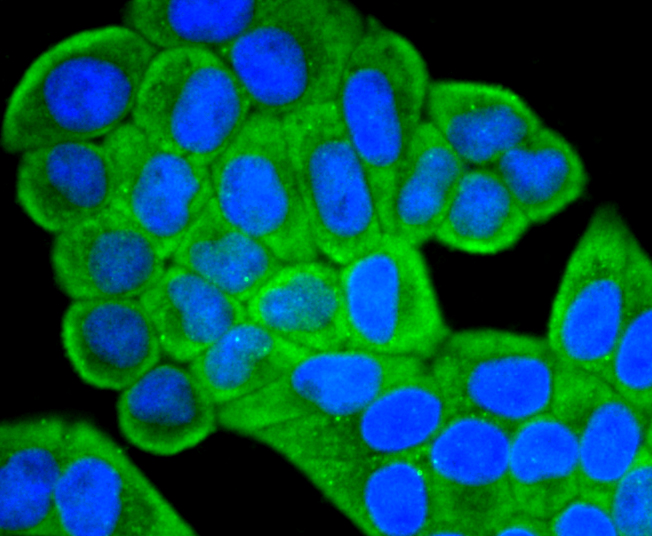
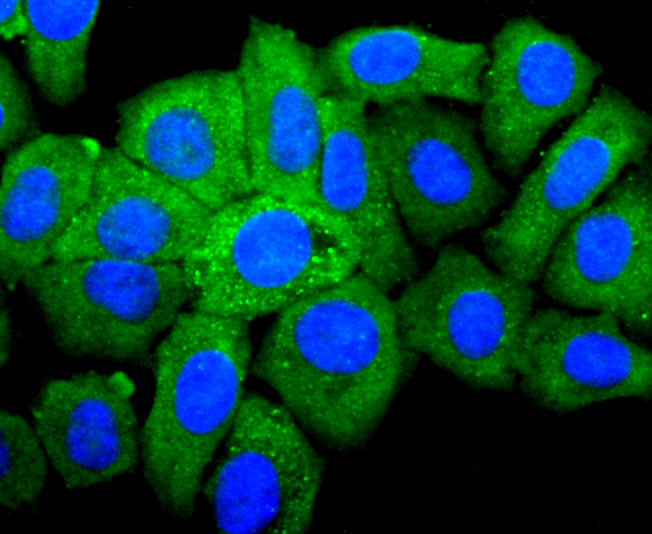
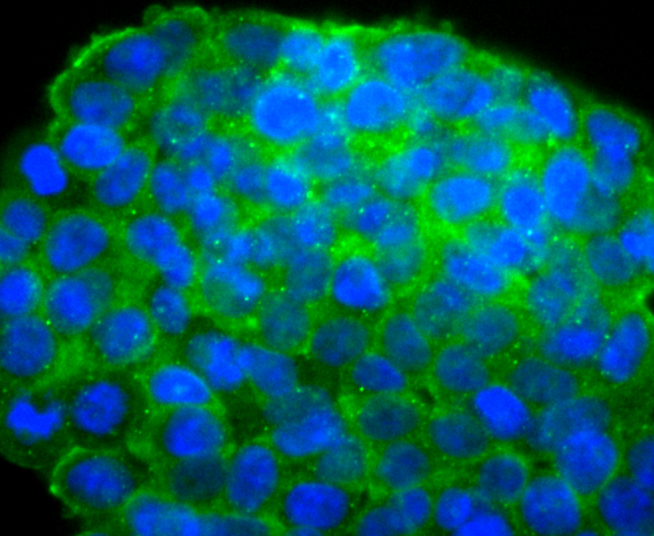
IGF-II (Insulin-like growth factor II; also multiplication-stimulating polypeptide/MSP and somatomedin-A) is a secreted 8 kDa polypeptide that belongs to the insulin family of peptide growth factors. It is part of a complex system of growth and metabolic-regulating proteins that is particularly important during development. It has been associated with nervous system proliferation and differentiation, myelination, adrenal cortical proliferation, and skeletal growth and differentiation. In human, IGF-II is primarily synthesized by the liver, and circulates at high levels in both fetus and adult. In rodent, however, IGF-II levels drop after the perinatal period, an effect attributed to the lack of a key gene promoter. This may indicate that postnatally, IGF-II has either a limited, or local effect only in rodent.