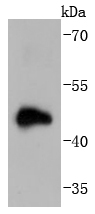
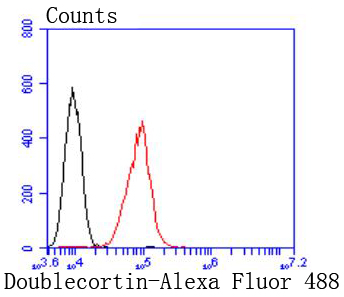
Lissencephaly (smooth brain) is an abnormality of brain development characterized by incomplete neuronal migration and a smooth cerebral surface, resulting in severe mental retardation. Genetic analysis identified two proteins that are mutated in some cases of lissencephaly, designated lissencephaly-1 protein (LIS1) and doublecortin. LIS1 shows sequence homology to β-subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Doublecortin contains a consensus Abl phosphorylation site, and it has some sequence homology to a predicted kinase protein. Both proteins are highly expressed in developing brain, suggesting that they may be involved in a signal transduction pathway that is crucial to brain development.