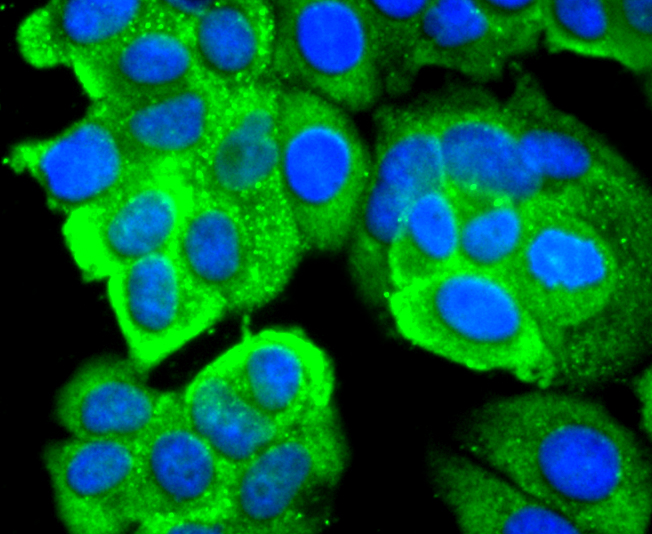
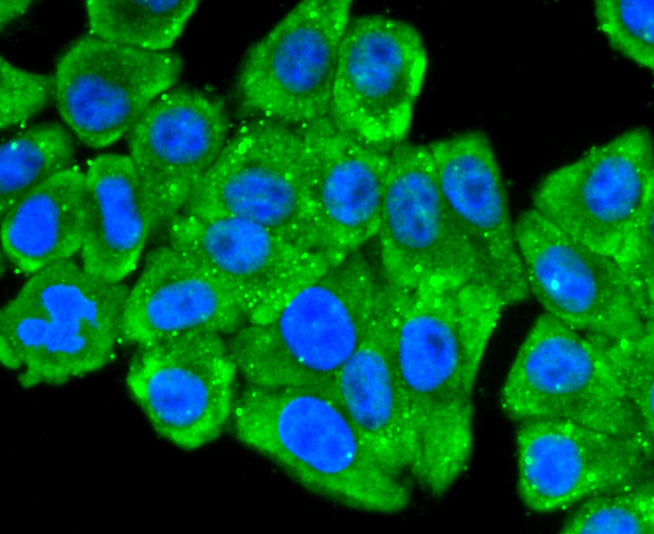
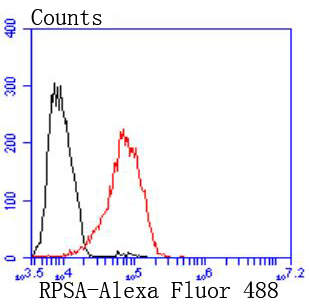
Laminin receptor (Laminin-R) has a heterodimeric structure similar to that of receptors for other extracellular matrix proteins such as Fibronectin and Vitronectin. Incorporation of Laminin-R into lysosomal membranes makes it possible for lysosomes to attach to surfaces coated with Laminin. This and other properties identify Laminin-R as a member of the integrin family of cell adhesion receptors. The Laminin-R precursor is a polypeptide whose expression is consistently upregulated in aggressive carcinoma. The precursor, which is also identified as p40 ribosome-associated protein, appears to be a multifunctional protein involved in the translational machinery. Laminin-R (also known as colon carcinoma laminin-binding protein) and is found at nine-fold higher levels in colon carcinoma than in adjacent normal colonic epithelium. Additionally, the level of the Laminin-R is higher in the lung cancer cell line than in the lung cell line.